Methanosarcina acetivorans utilizes a single NADPH-dependent thioredoxin system and contains additional thioredoxin homologues with distinct functions
- PMID: 27902413
- PMCID: PMC5903248
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.000406
Methanosarcina acetivorans utilizes a single NADPH-dependent thioredoxin system and contains additional thioredoxin homologues with distinct functions
Abstract
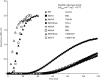
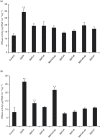
The thioredoxin system plays a central role in the intracellular redox maintenance in the majority of cells. The canonical system consists of an NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) and thioredoxin (Trx), a disulfide reductase. Although Trx is encoded in almost all sequenced genomes of methanogens, its incorporation into their unique physiology is not well understood. Methanosarcina acetivorans contains a single TrxR (MaTrxR) and seven Trx (MaTrx1-MaTrx7) homologues. We previously showed that MaTrxR and at least MaTrx7 compose a functional NADPH-dependent thioredoxin system. Here, we report the characterization of all seven recombinant MaTrxs. MaTrx1, MaTrx3, MaTrx4 and MaTrx5 lack appreciable disulfide reductase activity, unlike previously characterized MaTrx2, MaTrx6 and MaTrx7. Enzyme assays demonstrated that, of the MaTrxs, only the reduction of disulfide-containing MaTrx7 is linked to the oxidation of reduced coenzymes. NADPH is shown to be supplied to the MaTrxR-MaTrx7 system through the oxidation of the primary methanogen electron carriers F420H2 and ferredoxin, indicating that it serves as a primary intracellular reducing system in M. acetivorans. Bioinformatic analyses also indicate that the majority of methanogens likely utilize an NADPH-dependent thioredoxin system. The remaining MaTrxs may have specialized functions. MaTrx1 and MaTrx3 exhibited thiol oxidase activity. MaTrx3 and MaTrx6 are targeted to the membrane of M. acetivorans and likely function in the formation and the reduction of disulfides in membrane and/or extracellular proteins, respectively. This work provides insight into the incorporation of Trx into the metabolism of methanogens, and this reveals that methanogens contain Trx homologues with alternative properties and activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Catalytic Activity of the Archetype from Group 4 of the FTR-like Ferredoxin:Thioredoxin Reductase Family Is Regulated by Unique S = 7/2 and S = 1/2 [4Fe-4S] Clusters.Biochemistry. 2024 Jun 18;63(12):1588-1598. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00651. Epub 2024 May 31. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38817151 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the thioredoxin system from Methanosarcina acetivorans.FEBS J. 2014 Oct;281(20):4598-611. doi: 10.1111/febs.12964. Epub 2014 Sep 6. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 25112424 Free PMC article.
-
The Methanosarcina acetivorans thioredoxin system activates DNA binding of the redox-sensitive transcriptional regulator MsvR.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;42(6):965-9. doi: 10.1007/s10295-015-1592-y. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25791378 Free PMC article.
-
The thioredoxin reductase/thioredoxin system: novel redox targets for cancer therapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2005 Jan;4(1):6-13. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.1.1434. Epub 2004 Jan 8. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15684606 Review.
-
Role of thioredoxin in lung disease.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Apr;25(2):154-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2012.01.002. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22293327 Review.
Cited by
-
Catalytic Activity of the Archetype from Group 4 of the FTR-like Ferredoxin:Thioredoxin Reductase Family Is Regulated by Unique S = 7/2 and S = 1/2 [4Fe-4S] Clusters.Biochemistry. 2024 Jun 18;63(12):1588-1598. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00651. Epub 2024 May 31. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38817151 Free PMC article.
-
Toward a mechanistic and physiological understanding of a ferredoxin:disulfide reductase from the domains Archaea and Bacteria.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 15;293(24):9198-9209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002473. Epub 2018 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29720404 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of the Genus Methanohalophilus, Including a Newly Isolated Strain From Kebrit Deep in the Red Sea.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 24;10:839. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00839. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31068917 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure of the Apo-Form of NADPH-Dependent Thioredoxin Reductase from a Methane-Producing Archaeon.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Nov 17;7(11):166. doi: 10.3390/antiox7110166. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30453601 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Role of Multiple Thioredoxin Fold Proteins of Leptospirillum sp. in Oxidative Stress Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 10;21(5):1880. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051880. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32164170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferry JG. One-carbon metabolism in methanogenic anaerobes. In: Ljungdahl LL, Adams MW, Barton LL, Ferry JG, Johnson MK, editors. Biochemistry and Physiology of Anaerobic Bacteria. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2003. pp. 143–156. (editors)
-
- Zinder S. Physiological ecology of methanogens. In: Jerry JG, editor. Methanogenesis. New York, NY: Chapman and Hall; 1993. pp. 128–206. (editor)
-
- Ferry JG. Enzymology of one-carbon metabolism in methanogenic pathways. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1999;23:13–38. - PubMed
-
- Deppenmeier U. The membrane-bound electron transport system of Methanosarcina species. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004;36:55–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

