Efficacy and safety of penetration acupuncture on head for acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A randomized controlled study
- PMID: 27902622
- PMCID: PMC5134766
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005562
Efficacy and safety of penetration acupuncture on head for acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A randomized controlled study
Abstract
Background: Acupuncture, especially acupuncture treatment on head for acute intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), has long been disputable. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of penetration acupuncture on head in patients with acute ICH.
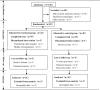
Methods: Eighty-two patients with acute ICH were randomized to receive penetration acupuncture treatment on head combined with conventional treatment (treatment group [TG]) or conventional treatment only (control group [CG]). Acupuncture treatments were given in 24 sessions over 4 weeks, with 3-month follow-up period. Measures included Clinical Neurological Function Deficit Scale (CNFDS), Barthel Index (BI), vital signs (respiration, heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation), and hematoma absorption ratio.
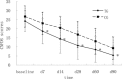
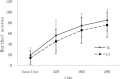
Results: Both groups showed a progressively improvement in CNFDS and BI scores from day 7 to 90. The TG showed a significantly greater improvement in CNFDS than CG over time (P < 0.05). However, BI failed to show significant difference between the 2 groups (P > 0.05). The vital signs were stable and no expansion of hematoma occurred over the course of acupuncture treatment.
Conclusion: Penetration acupuncture treatment on head appeared to be safe over the course of treatment on acute ICH and may result in additional functional improvements detected in the CNFDS but not reflected in the BI. A larger-scale clinical trial with longer follow-up assessments is required to confirm these findings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, et al. Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol 2003;2:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Mayer SA, Brun NC, Begtrup K, et al. Recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 2005;352:777–85. - PubMed
-
- Jiang B, Wang WZ, Chen H, et al. Incidence and trends of stroke and its subtypes in China: results from three large cities. Stroke 2006;37:63–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

