EphA2 is a functional receptor for the growth factor progranulin
- PMID: 27903606
- PMCID: PMC5146997
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201603079
EphA2 is a functional receptor for the growth factor progranulin
Abstract
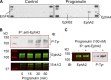
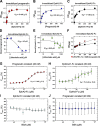
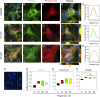
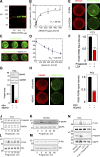
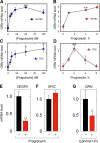
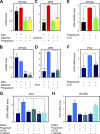
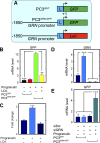
Although the growth factor progranulin was discovered more than two decades ago, the functional receptor remains elusive. Here, we discovered that EphA2, a member of the large family of Ephrin receptor tyrosine kinases, is a functional signaling receptor for progranulin. Recombinant progranulin bound with high affinity to EphA2 in both solid phase and solution. Interaction of progranulin with EphA2 caused prolonged activation of the receptor, downstream stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt, and promotion of capillary morphogenesis. Furthermore, we found an autoregulatory mechanism of progranulin whereby a feed-forward loop occurred in an EphA2-dependent manner that was independent of the endocytic receptor sortilin. The discovery of a functional signaling receptor for progranulin offers a new avenue for understanding the underlying mode of action of progranulin in cancer progression, tumor angiogenesis, and perhaps neurodegenerative diseases.
© 2016 Neill et al.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed Z., Sheng H., Xu Y.F., Lin W.L., Innes A.E., Gass J., Yu X., Wuertzer C.A., Hou H., Chiba S., et al. 2010. Accelerated lipofuscinosis and ubiquitination in granulin knockout mice suggest a role for progranulin in successful aging. Am. J. Pathol. 177:311–324. 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090915 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker M., Mackenzie I.R., Pickering-Brown S.M., Gass J., Rademakers R., Lindholm C., Snowden J., Adamson J., Sadovnick A.D., Rollinson S., et al. 2006. Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature. 442:916–919. 10.1038/nature05016 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

