NK cells converge lytic granules to promote cytotoxicity and prevent bystander killing
- PMID: 27903610
- PMCID: PMC5166499
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201604136
NK cells converge lytic granules to promote cytotoxicity and prevent bystander killing
Abstract
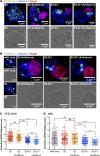
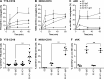
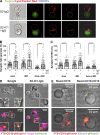
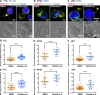
Natural killer (NK) cell activation triggers sequential cellular events leading to destruction of diseased cells. We previously identified lytic granule convergence, a dynein- and integrin signal-dependent movement of lysosome-related organelles to the microtubule-organizing center, as an early step in the cell biological process underlying NK cell cytotoxicity. Why lytic granules converge during NK cell cytotoxicity, however, remains unclear. We experimentally controlled the availability of human ligands to regulate NK cell signaling and promote granule convergence with either directed or nondirected degranulation. By the use of acoustic trap microscopy, we generated specific effector-target cell arrangements to define the impact of the two modes of degranulation. NK cells with converged granules had greater targeted and less nonspecific "bystander" killing. Additionally, NK cells in which dynein was inhibited or integrin blocked under physiological conditions demonstrated increased nondirected degranulation and bystander killing. Thus, NK cells converge lytic granules and thereby improve the efficiency of targeted killing and prevent collateral damage to neighboring healthy cells.
© 2016 Hsu et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rapid activation receptor- or IL-2-induced lytic granule convergence in human natural killer cells requires Src, but not downstream signaling.Blood. 2013 Apr 4;121(14):2627-37. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-437012. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23380740 Free PMC article.
-
Different NK cell-activating receptors preferentially recruit Rab27a or Munc13-4 to perforin-containing granules for cytotoxicity.Blood. 2009 Nov 5;114(19):4117-27. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225359. Epub 2009 Aug 24. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19704116
-
Single Degranulations in NK Cells Can Mediate Target Cell Killing.J Immunol. 2018 May 1;200(9):3231-3243. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701500. Epub 2018 Mar 28. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29592963 Free PMC article.
-
Locked and Loaded: Mechanisms Regulating Natural Killer Cell Lytic Granule Biogenesis and Release.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 26;13:871106. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.871106. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35558071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular regulation of the plasma membrane-proximal cellular steps involved in NK cell cytolytic function.J Cell Sci. 2020 Feb 21;133(5):jcs240424. doi: 10.1242/jcs.240424. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32086255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Kinase C δ Regulates the Depletion of Actin at the Immunological Synapse Required for Polarized Exosome Secretion by T Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 26;10:851. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00851. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31105694 Free PMC article.
-
Fc γ receptor IIIa/CD16a processing correlates with the expression of glycan-related genes in human natural killer cells.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100183. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015516. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33310702 Free PMC article.
-
17-Hydroxyprogesterone caproate improves T cells and NK cells in response to placental ischemia; new mechanisms of action for an old drug.Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020 Jan;19:226-232. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2019.11.005. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 31806502 Free PMC article.
-
Human NK cells: From development to effector functions.Innate Immun. 2021 Apr;27(3):212-229. doi: 10.1177/17534259211001512. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Innate Immun. 2021. PMID: 33761782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b) mutation causes dysregulated human natural killer cell maturation and impaired lytic function.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Jan;145(1):345-357.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.09.016. Epub 2019 Oct 7. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31600547 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

