CDH1 regulates E2F1 degradation in response to differentiation signals in keratinocytes
- PMID: 27903963
- PMCID: PMC5354885
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13636
CDH1 regulates E2F1 degradation in response to differentiation signals in keratinocytes
Abstract
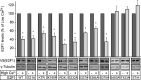
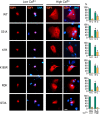
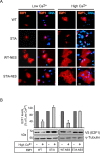
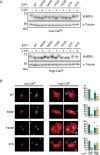
The E2F1 transcription factor plays key roles in skin homeostasis. In the epidermis, E2F1 expression is essential for normal proliferation of undifferentiated keratinocytes, regeneration after injury and DNA repair following UV radiation-induced photodamage. Abnormal E2F1 expression promotes nonmelanoma skin carcinoma. In addition, E2F1 must be downregulated for proper keratinocyte differentiation, but the relevant mechanisms involved remain poorly understood. We show that differentiation signals induce a series of post-translational modifications in E2F1 that are jointly required for its downregulation. Analysis of the structural determinants that govern these processes revealed a central role for S403 and T433. In particular, substitution of these two amino acid residues with non-phosphorylatable alanine (E2F1 ST/A) interferes with E2F1 nuclear export, K11- and K48-linked polyubiquitylation and degradation in differentiated keratinocytes. In contrast, replacement of S403 and T433 with phosphomimetic aspartic acid to generate a pseudophosphorylated E2F1 mutant protein (E2F1 ST/D) generates a protein that is regulated in a manner indistinguishable from that of wild type E2F1. Cdh1 is an activating cofactor that interacts with the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) ubiquitin E3 ligase, promoting proteasomal degradation of various substrates. We found that Cdh1 associates with E2F1 in keratinocytes. Inhibition or RNAi-mediated silencing of Cdh1 prevents E2F1 degradation in response to differentiation signals. Our results reveal novel regulatory mechanisms that jointly modulate post-translational modifications and downregulation of E2F1, which are necessary for proper epidermal keratinocyte differentiation.
Keywords: E2F1; epidermis; keratinocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of p38- and CRM1-dependent nuclear export promotes E2F1 degradation during keratinocyte differentiation.Oncogene. 2007 Feb 22;26(8):1147-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209894. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16924238
-
Phosphorylation by p38 MAP kinase is required for E2F1 degradation and keratinocyte differentiation.Oncogene. 2009 Jan 8;28(1):52-62. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.354. Epub 2008 Sep 15. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 18794805
-
Regulation of E2F1 by APC/C Cdh1 via K11 linkage-specific ubiquitin chain formation.Cell Cycle. 2012 May 15;11(10):2030-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.20643. Epub 2012 May 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22580462 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 19;18(10):2188. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102188. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29048367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering mechanisms of nuclear degradation in keratinocytes: A paradigm for nuclear degradation in other tissues.Nucleus. 2018 Jan 1;9(1):56-64. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2017.1412027. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Nucleus. 2018. PMID: 29205081 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation stabilizes E2F1 protein by suppressing binding of the FBXW7 ubiquitin ligase subunit.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 8;121(41):e2414618121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2414618121. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39361641 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin in psoriasis and its comorbidities: a review.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Aug 9;20(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01510-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34372872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex Cartography: Regulation of E2F Transcription Factors by Cyclin F and Ubiquitin.Trends Cell Biol. 2020 Aug;30(8):640-652. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.05.002. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Trends Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32513610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin F Controls Cell-Cycle Transcriptional Outputs by Directing the Degradation of the Three Activator E2Fs.Mol Cell. 2019 Jun 20;74(6):1264-1277.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.010. Epub 2019 May 23. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31130363 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Kindlin-2 in Cutaneous Squamous Carcinoma Cell Migration and Proliferation: Implications for Tumour Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 1;26(15):7426. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157426. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghari F, Quirke AM, Munro S, Kawalkowska J, Picaud S, McGouran J, Subramanian V, Muth A, Williams R, Kessler B, Thompson PR, Fillipakopoulos P, Knapp S, Venables PJ, La Thangue NB. Citrullination-acetylation interplay guides E2F-1 activity during the inflammatory response. Science advances. 2016;2:e1501257. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhan L, Huang C, Meng XM, Song Y, Wu XQ, Miu CG, Zhan XS, Li J. Promising roles of mammalian E2Fs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Signal. 2014;26:1075–1081. - PubMed
-
- D’Souza SJ, Pajak A, Balazsi K, Dagnino L. Ca2+ and BMP-6 signaling regulate E2F during epidermal keratinocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:23531–23538. - PubMed
-
- Dagnino L, Fry CJ, Bartley SM, Farnham P, Gallie BL, Phillips RA. Expression patterns of the E2F family of transcription factors during mouse nervous system development. Mech Dev. 1997;66:13–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

