Increased Set1 binding at the promoter induces aberrant epigenetic alterations and up-regulates cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element modulator alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 27904655
- PMCID: PMC5122196
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0294-2
Increased Set1 binding at the promoter induces aberrant epigenetic alterations and up-regulates cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element modulator alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Up-regulated cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element modulator α (CREMα) which can inhibit IL-2 and induce IL-17A in T cells plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This research aimed to investigate the mechanisms regulating CREMα expression in SLE.
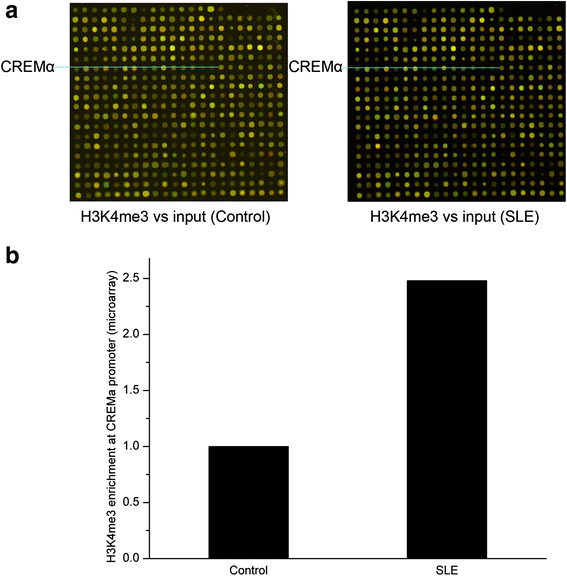
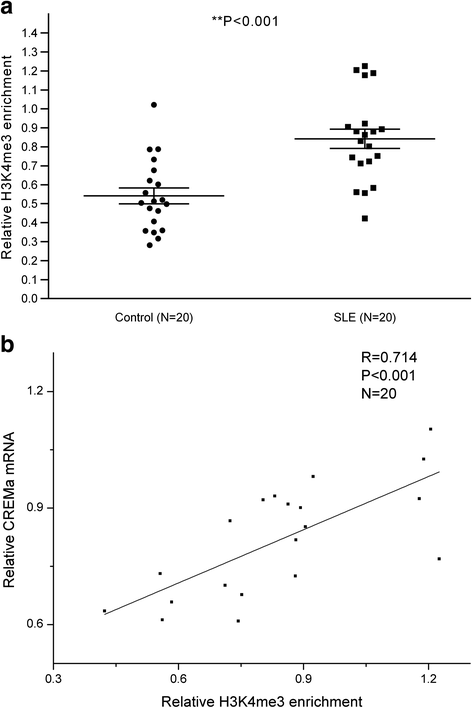
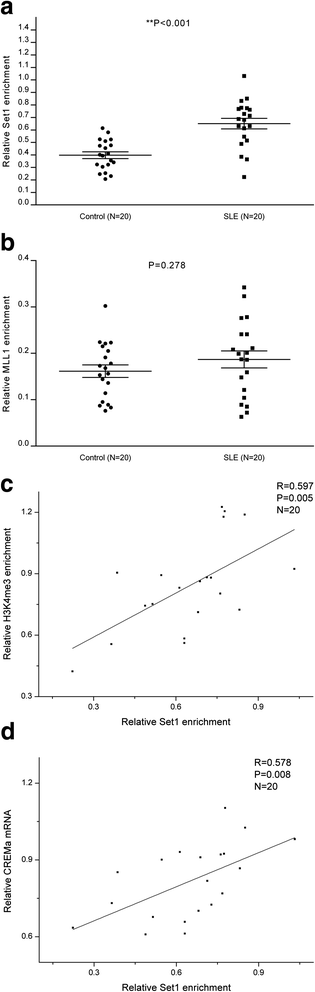
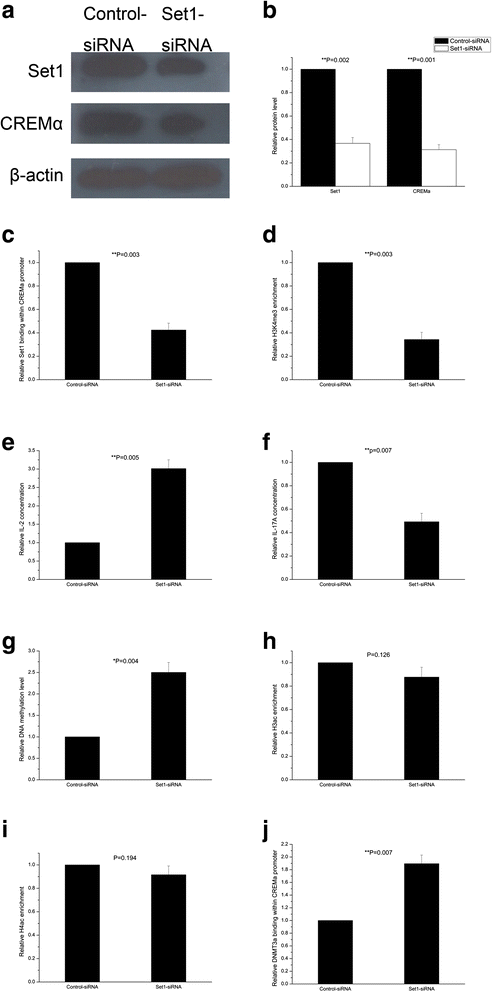
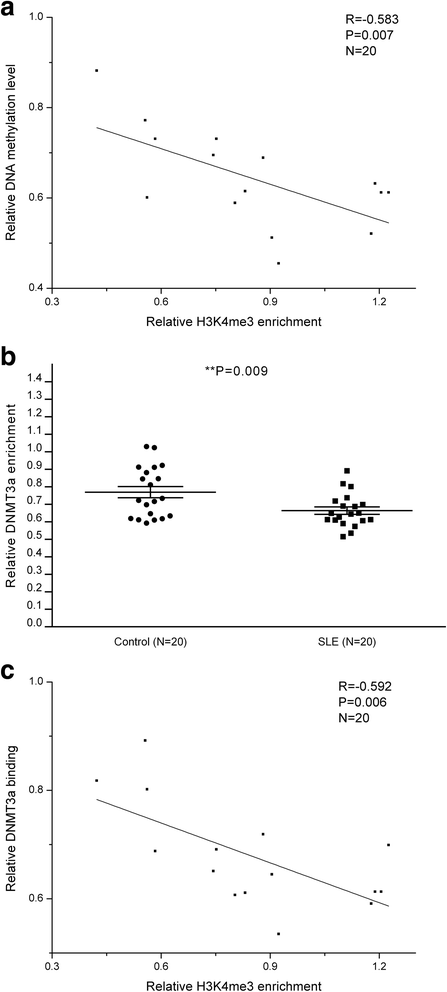
Results: From the chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) microarray data, we found a sharply increased H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) amount at the CREMα promoter in SLE CD4+ T cells compared to controls. Then, by ChIP and real-time PCR, we confirmed this result. Moreover, H3K4me3 amount at the promoter was positively correlated with CREMα mRNA level in SLE CD4+ T cells. In addition, a striking increase was observed in SET domain containing 1 (Set1) enrichment, but no marked change in mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1) enrichment at the CREMα promoter in SLE CD4+ T cells. We also proved Set1 enrichment was positively correlated with both H3K4me3 amount at the CREMα promoter and CREMα mRNA level in SLE CD4+ T cells. Knocking down Set1 with siRNA in SLE CD4+ T cells decreased Set1 and H3K4me3 enrichments, and elevated the levels of DNMT3a and DNA methylation, while the amounts of H3 acetylation (H3ac) and H4 acetylation (H4ac) didn't alter greatly at the CREMα promoter. All these changes inhibited the expression of CREMα, then augmented IL-2 and down-modulated IL-17A productions. Subsequently, we observed that DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) 3a enrichment at the CREMα promoter was down-regulated significantly in SLE CD4+ T cells, and H3K4me3 amount was negatively correlated with both DNA methylation level and DNMT3a enrichment at the CREMα promoter in SLE CD4+ T cells.
Conclusions: In SLE CD4+ T cells, increased Set1 enrichment up-regulates H3K4me3 amount at the CREMα promoter, which antagonizes DNMT3a and suppresses DNA methylation within this region. All these factors induce CREMα overexpression, consequently result in IL-2 under-expression and IL-17A overproduction, and contribute to SLE at last. Our findings provide a novel approach in SLE treatment.
Keywords: CREMα; DNA methylation; DNMT3a; H3K4me3; Set1; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of aberrant H3K27me3 modification in promoter regions on cAMP response element modulator α expression in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017 Dec 20;37(12):1597-1602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.12.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 29292251 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Decreased SUV39H1 at the promoter region leads to increased CREMα and accelerates autoimmune response in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Dec 20;14(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01411-7. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36536372 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α protein induces interleukin 17A expression and mediates epigenetic alterations at the interleukin-17A gene locus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43437-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.299313. Epub 2011 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22025620 Free PMC article.
-
[Interleukin-2 signaling pathway regulating molecules in systemic lupus erythematosus].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Dec 18;48(6):1100-1104. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27987522 Review. Chinese.
-
cAMP responsive element modulator: a critical regulator of cytokine production.Trends Mol Med. 2013 Apr;19(4):262-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23491535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis on Abnormal Methylome of Differentially Expressed Genes and Disease Pathways in the Immune Cells of RA and SLE.Front Immunol. 2021 May 17;12:668007. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668007. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34079550 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation changes on immune cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Autoimmunity. 2020 May;53(3):114-121. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2020.1722108. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Autoimmunity. 2020. PMID: 32019373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant RNA Splicing Events Driven by Mutations of RNA-Binding Proteins as Indicators for Skin Cutaneous Melanoma Prognosis.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 15;10:568469. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.568469. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33178596 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Epigenetic Changes Underlying Autoimmunity.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Mar;36(7-9):423-440. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0066. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34544258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effect of aberrant H3K27me3 modification in promoter regions on cAMP response element modulator α expression in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017 Dec 20;37(12):1597-1602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.12.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 29292251 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

