Astragaloside IV enhances cardioprotection of remote ischemic conditioning after acute myocardial infarction in rats
- PMID: 27904669
- PMCID: PMC5126311
Astragaloside IV enhances cardioprotection of remote ischemic conditioning after acute myocardial infarction in rats
Abstract
Background: Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) has been shown to be a practical method for protecting the heart from ischemic/reperfusion (I/R) injury. In the present study, we investigated whether or not the combination of RIC and Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) could improve cardioprotection against acute myocardial infarction (AMI)-induced heart failure (HF) when compared with individual treatments.
Material and methods: A rat model of AMI was established via permanent ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD). Postoperatively, the rats were randomly grouped into a sham group (n=10), a model group (n=15), an AS-IV alone group (n=15), an RIC alone group (n=15) and a combined treatment group (AS-IV+RIC; n=15). All treatments were administered for 2 weeks.
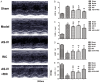
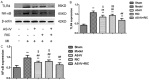
Results: After treatment for 2 weeks, the survival rate was improved, the cardiac function was preserved and the infarcted size was limited in AS-IV alone and RIC alone treatment groups compared to the model group, whereas the combined treatment yielded the most optimal protective effects. Additional studies suggested that AS-IV enhanced the cardioprotective effects of RIC by alleviating myocardial fibrosis, suppressing inflammation, attenuating apoptosis and ameliorating impairment of the myocardial ultrastructural.
Conclusion: AS-IV enhances the cardioprotective effects of RIC against AMI-induced HF and ventricular remodeling, which represents a potential therapeutic approach for preserving cardiac function and improving the prognosis of AMI.
Keywords: Astragaloside IV; acute myocardial infarction; cardioprotection; remote ischemic conditioning; ventricular remodeling.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Cardioprotective Effects of Remote Ischemic Conditioning in a Rat Model of Acute Myocardial Infarction.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Mar 8;25:1769-1779. doi: 10.12659/MSM.914916. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30848248 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated remote ischemic conditioning attenuates left ventricular remodeling via exosome-mediated intercellular communication on chronic heart failure after myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol. 2015 Jan 15;178:239-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.10.144. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25464262
-
Remote cyclic compression ameliorates myocardial infarction injury in rats via AMPK-dependent pathway.Microvasc Res. 2022 May;141:104313. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2022.104313. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Microvasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35041850
-
Remote ischemic conditioning: the cardiologist's perspective.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2012 Nov;13(11):667-74. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e328357bff2. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2012. PMID: 23114270 Review.
-
Influence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Comorbidities, Medication Use and Procedural Variables on Remote Ischemic Conditioning Efficacy in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 2;20(13):3246. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133246. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31269650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The protective effects of different compatibility proportions of the couplet medicines for Astragali Radix and Angelica sinensis Radix on myocardial infarction injury.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):165-175. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1725581. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 32608342 Free PMC article.
-
A Preclinical Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Astragaloside IV for Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Front Physiol. 2018 Jul 3;9:795. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00795. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30018562 Free PMC article.
-
Immune and inflammatory mechanism of remote ischemic conditioning: A narrative review.Brain Circ. 2023 Jun 30;9(2):77-87. doi: 10.4103/bc.bc_57_22. eCollection 2023 Apr-Jun. Brain Circ. 2023. PMID: 37576576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogel encapsulating gold nanoparticles for targeted delivery of nitroglycerin to reduce post-cardiac dysfunction inflammation by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Dec;32(6):3899-3911. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01580-2. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39443402
-
Potential traditional Chinese medicines with anti-inflammation in the prevention of heart failure following myocardial infarction.Chin Med. 2023 Mar 17;18(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00732-w. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36932409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–60. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Ajani UA, Croft JB, Critchley JA, Labarthe DR, Kottke TE, Giles WH, Capewell S. Explaining the decrease in U. S. deaths from coronary disease, 1980-2000. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2388–2398. - PubMed
-
- Ram CV. Angiotensin receptor blockers: current status and future prospects. Am J Med. 2008;121:656–663. - PubMed
-
- Ibanez B, Macaya C, Sanchez-Brunete V, Pizarro G, Fernandez-Friera L, Mateos A, Fernandez-Ortiz A, Garcia-Ruiz JM, Garcia-Alvarez A, Iniguez A, Jimenez-Borreguero J, Lopez-Romero P, Fernandez-Jimenez R, Goicolea J, Ruiz-Mateos B, Bastante T, Arias M, Iglesias-Vazquez JA, Rodriguez MD, Escalera N, Acebal C, Cabrera JA, Valenciano J, Perez de Prado A, Fernandez-Campos MJ, Casado I, Garcia-Rubira JC, Garcia-Prieto J, Sanz-Rosa D, Cuellas C, Hernandez-Antolin R, Albarran A, Fernandez-Vazquez F, de la Torre-Hernandez JM, Pocock S, Sanz G, Fuster V. Effect of early metoprolol on infarct size in ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: the Effect of Metoprolol in Cardioprotection During an Acute Myocardial Infarction (METOCARD-CNIC) trial. Circulation. 2013;128:1495–1503. - PubMed
-
- Otani H. Ischemic preconditioning: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10:207–247. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
