Hyperbaric oxygen protects mandibular condylar chondrocytes from interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 27904712
- PMCID: PMC5126354
Hyperbaric oxygen protects mandibular condylar chondrocytes from interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
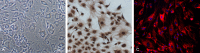
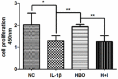
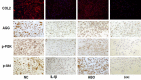
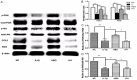
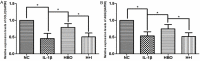
Objectives: Mandibular condylar chondrocyte apoptosis is mainly responsible for the development and progression of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis (TMJ-OA). Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) generally serves an agent that induces chondrocyte apoptosis. Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) treatment increases proteoglycan synthesis in vivo. We explore the protective effect of HBO on IL-1β-induced mandibular condylar chondrocyte apoptosis in rats and the potential molecular mechanisms. Methods: Chondrocytes were isolated from the TMJ of 3-4-week old Sprague-Dawley rats. The Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay was used to determine cell viability. The phosphorylated phosphoinositide-3 kinase (p-PI3K), phosphorylated AKT (p-Akt), type II collagen (COL2), and aggrecan (AGG) content was detected by immunofluorescence, immunocytochemistry and western blotting. The expression of Pi3k, Akt, Col2 and Agg mRNA was measured using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Results: HBO inhibited the cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by IL-1β (10 ng/mL) in the mandibular condylar chondrocytes. HBO also decreased the IL-1β activity that decreased p-PI3K and p-AKT levels, and increased COL2 and AGG expression, with the net effect of suppressing extracellular matrix degradation. Conclusions: These data suggest that HBO may protect mandibular condylar chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and that it may promote the expression of mandibular condylar chondrocyte extracellular matrix through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: Hyperbaric oxygen; IL-1β; PI3K/AKT signaling; extracellular matrix.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyperbaric oxygen protects type II collagen in interleukin-1β-induced mandibular condylar chondrocyte via inhibiting the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 17;8(36):60312-60323. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19294. eCollection 2017 Sep 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28947973 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin protects chondrocytes from interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis by regulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jan 1;8(1):298-308. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25755716 Free PMC article.
-
Calycosin prevents IL-1β-induced articular chondrocyte damage in osteoarthritis through regulating the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022 Jun;58(6):491-502. doi: 10.1007/s11626-022-00694-7. Epub 2022 Jun 15. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022. PMID: 35705795
-
Protection of ginsenoside Rg1 on chondrocyte from IL-1β-induced mitochondria-activated apoptosis through PI3K/Akt signaling.Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 Jul;392(1-2):249-57. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2035-1. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24671491
-
Requirement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway for the effect of nicotine on interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat model of osteoarthritis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jul 6;423(3):606-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.045. Epub 2012 Jun 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22713471
Cited by
-
Hyperbaric oxygen protects type II collagen in interleukin-1β-induced mandibular condylar chondrocyte via inhibiting the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 17;8(36):60312-60323. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19294. eCollection 2017 Sep 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28947973 Free PMC article.
-
Survey of Molecular Mechanisms of Hyperbaric Oxygen in Tissue Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11754. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111754. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of β-catenin signaling in aggrecan-expressing cells in temporomandibular joint causes osteoarthritis-like defects.Int J Oral Sci. 2018 Apr 23;10(2):13. doi: 10.1038/s41368-018-0016-z. Int J Oral Sci. 2018. PMID: 29686224 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of the semaphorin family in cartilage and osteoarthritis.Histochem Cell Biol. 2024 Sep;162(3):187-202. doi: 10.1007/s00418-024-02303-y. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Histochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38849589 Review.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia decreases pulmonary clearance of 99mTc-labelled particulate matter in mice.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Jun 15;9(6):3060-3072. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28670393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scrivani SJ, Keith DA, Kaban LB. Temporomandibular disorders. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2693–2705. - PubMed
-
- Aida Y, Maeno M, Suzuki N, Shiratsuchi H, Motohashi M, Matsumura H. The effect of IL-1beta on the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in human chondrocytes. Life Sci. 2005;77:3210–3221. - PubMed
-
- Zhou PH, Liu SQ, Peng H. The effect of hyaluronic acid on IL-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat model of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2008;26:1643–1648. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Armada MJ, Carames B, Lires-Dean M, Cillero-Pastor B, Ruiz-Romero C, Galdo F, Blanco FJ. Cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta, differentially regulate apoptosis in osteoarthritis cultured human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14:660–669. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
