The role of PIM1 in the ibrutinib-resistant ABC subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 27904766
- PMCID: PMC5126268
The role of PIM1 in the ibrutinib-resistant ABC subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
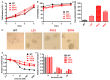
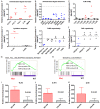
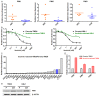
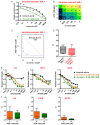
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a heterogeneous lymphoma and the most common subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, accounting for roughly 30% of newly diagnosed cases in the United States. DLBCL can be separated into the activated B cell-like (ABC) and germinal center B cell-like (GCB) subtypes, with distinct gene expression profiles, oncogenic aberrations, and clinical outcomes. ABC-DLBCL is characterized by chronically active B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling that can be modulated by Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) activity. Thus, BTK serves as an attractive therapeutic target in this type of B-cell malignancy. Ibrutinib, a first-in-class, orally available covalent BTK inhibitor, has demonstrated clinical activity in several B-cell leukemias and lymphomas. A phase 1/2 clinical trial of single-agent ibrutinib in relapsed and refractory DLBCL patients revealed an overall response rate of 37% in ABC-DLBCL patients. However, responses to kinase-directed therapies are often limited by emerging resistance mechanisms that bypass the therapeutic target. Here we report the discovery of point mutations within the kinase PIM1 that reduce sensitivity to ibrutinib in ABC-DLBCL. These mutations stabilize PIM1 and affect upstream regulators and downstream targets of NF-κB signaling. The introduction of mutant PIM1 into an ABC-DLBCL cell line, TMD8, increased colony formation and decreased sensitivity to ibrutinib. In addition, ibrutinib-resistant cell lines generated by prolonged ibrutinib exposure in vitro upregulated PIM1 expression, consistent with a role for PIM1 in antagonizing ibrutinib activity. The combination of a pan-PIM inhibitor with ibrutinib synergistically inhibited proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Together, these data provide a rationale for combining BTK and PIM1 inhibition in the treatment of ABC-DLBCL.
Keywords: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; DLBCL; PIM1; ibrutinib.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Naquotinib exerts antitumor activity in activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Leuk Res. 2020 Jan;88:106286. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2019.106286. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Leuk Res. 2020. PMID: 31865062
-
Combinatorial BTK and MALT1 inhibition augments killing of CD79 mutant diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):42232-42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6273. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26540570 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Enzastaurin and Ibrutinib synergistically induces anti-tumor effects in diffuse large B cell lymphoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 18;38(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1076-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30777096 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Semin Hematol. 2015 Apr;52(2):77-85. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Semin Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25805587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0779-z. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole exome sequencing identifies mutational signatures of vitreoretinal lymphoma.Haematologica. 2020 Sep 1;105(9):e458-460. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.233783. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 33054063 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The targetable kinase PIM1 drives ALK inhibitor resistance in high-risk neuroblastoma independent of MYCN status.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 28;10(1):5428. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13315-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31780656 Free PMC article.
-
Role and mechanism of PIM family in the immune microenvironment of diffuse large B cell lymphoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Mar 4;21(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-02947-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36871027 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-independent, autonomous B cell receptor signaling drives activated B cell DLBCL.J Exp Med. 2024 May 6;221(5):e20230941. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230941. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38512136 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Genomic Alteration in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma and the Expression of Some Related Genes.Neoplasia. 2018 Oct;20(10):1059-1069. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Neoplasia. 2018. PMID: 30227305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsukada S, Saffran DC, Rawlings DJ, Parolini O, Allen RC, Klisak I, Sparkes RS, Kubagawa H, Mohandas T, Quan S, Belmont JW, Cooper MD, Conley ME, Witte ON. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993;72:279–290. - PubMed
-
- Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Tolar P, Young RM, Romesser PB, Kohlhammer H, Lamy L, Zhao H, Yang Y, Xu W, Shaffer AL, Wright G, Xiao W, Powell J, Jiang JK, Thomas CJ, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM, Johnson NA, Rimsza LM, Campo E, Jaffe ES, Wilson WH, Delabie J, Smeland EB, Fisher RI, Braziel RM, Tubbs RR, Cook JR, Weisenburger DD, Chan WC, Pierce SK, Staudt LM. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 2010;463:88–92. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herman SE, Gordon AL, Hertlein E, Ramanunni A, Zhang X, Jaglowski S, Flynn J, Jones J, Blum KA, Buggy JJ, Hamdy A, Johnson AJ, Byrd JC. Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by PCI-32765. Blood. 2011;117:6287–6296. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cinar M, Hamedani F, Mo Z, Cinar B, Amin HM, Alkan S. Bruton tyrosine kinase is commonly overexpressed in mantle cell lymphoma and its attenuation by Ibrutinib induces apoptosis. Leuk Res. 2013;37:1271–1277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
