THE NINE TEST SCREENING BATTERY - NORMATIVE VALUES ON A GROUP OF RECREATIONAL ATHLETES
- PMID: 27904795
- PMCID: PMC5095945
THE NINE TEST SCREENING BATTERY - NORMATIVE VALUES ON A GROUP OF RECREATIONAL ATHLETES
Abstract
Background: A variety of risk factors predispose athletes to injury, such as impaired neuromuscular control, insufficient core stability, and muscular imbalances. The goal of assessing functional movement patterns is to detect imbalances and correct them with prevention strategies and thereby decrease injuries, and improve performance and quality of life.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to generate normative values for the 'Nine Test Screening Battery' (9TSB) in a group of recreational athletes. A secondary aim was to study gender differences and differences between subjects with (more than six weeks before test occasion) and without previous injury (regardless of injury location). A third aim was to investigate the psychometric properties of the 9TSB.
Methods: Eighty healthy recreational athletes, (40 men and 40 women) aged 22-58, were included. The subjects were tested according to strict criteria during nine functional movement exercises that comprise the 9TSB; each graded using a ordinal scale of 0-3, at one occasion. The maximum possible score is 27 points.
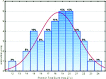
Results: The median score for the whole group was 18 (Range 12 - 24). A normal distribution of the test scores, with no floor-ceiling effects was found. There was no significant gender difference (p = 0.16) or difference between the group that reported previous injuries (regardless of injury location) and the group that did not (p = 0.65). The internal consistency was 0.41 with Cronbach's alpha.
Conclusion: A normal distribution of test results with no floor-ceiling effect was found. History of previous injury (more than six weeks before testing) or gender did not affect the results. In order to determine and cut scores for what is considered optimal or dysfunctional movement patterns, further cohort studies are required.
Keywords: Clinical test; functional movement; movement pattern; screening.
Figures



References
-
- Blair S. Physical inactivity: The biggest public health problem of the 21st Century. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43:1-2. - PubMed
-
- Svenska Friidrottsförbundets årsberättelse. (2013) From: http://www.friidrott.se/docs/arsberatt13.pdf 2014-07-01.
-
- Zazulak B Cholewicki J Reeves NP. Neuromuscular control of trunk stability: clinical implications for sports injury prevention. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2008;16:497–505. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
