Imaging of patellar fractures
- PMID: 27905071
- PMCID: PMC5265199
- DOI: 10.1007/s13244-016-0535-0
Imaging of patellar fractures
Abstract
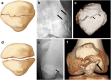
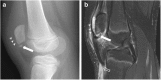
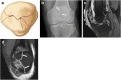
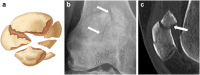
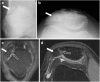
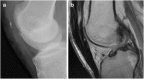
Patellar fractures account for approximately 1% of all skeletal fractures and may result from direct, indirect, or combined trauma. Because of the importance of patellar integrity for knee extension and the risk of associated injury to the extensor mechanism, accurate reporting and description of fracture type is paramount for appropriate management. This pictorial essay aims to review the normal anatomy of the patella, the mechanisms of injury and different types of patellar fractures, with a brief introduction to therapeutic management. Teaching Points • Patellar fractures are classified according to their morphology and degree of displacement.• Direct trauma results in stellate fractures.• Indirect trauma results in transverse fractures.• Displacement should raise suspicion for retinacular injury.
Keywords: Conventional radiograph; Extensor mechanism rupture; Fracture; MRI; Patella.
Figures








References
-
- Melvin JS, Karunakar MA. Patella fractures and extensor mechanism injuries. In: Court-Brown CB, Heckman JD, McQueen MM, Ricci WM, Tornetta P III, editors. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in adults. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2004. pp. 2269–2302.
-
- Pengas IP, Assiotis A, Khan W, Spalding T. Adult native knee extensor mechanism ruptures. Injury. 2016 - PubMed
-
- Scapinelli R. Blood supply of the human patella. Its relation to ischaemic necrosis after fracture. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 1967;49:563–570. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

