Development of a measure of model fidelity for mental health Crisis Resolution Teams
- PMID: 27905909
- PMCID: PMC5133753
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-016-1139-4
Development of a measure of model fidelity for mental health Crisis Resolution Teams
Abstract
Background: Crisis Resolution Teams (CRTs) provide short-term intensive home treatment to people experiencing mental health crisis. Trial evidence suggests CRTs can be effective at reducing hospital admissions and increasing satisfaction with acute care. When scaled up to national level however, CRT implementation and outcomes have been variable. We aimed to develop and test a fidelity scale to assess adherence to a model of best practice for CRTs, based on best available evidence.
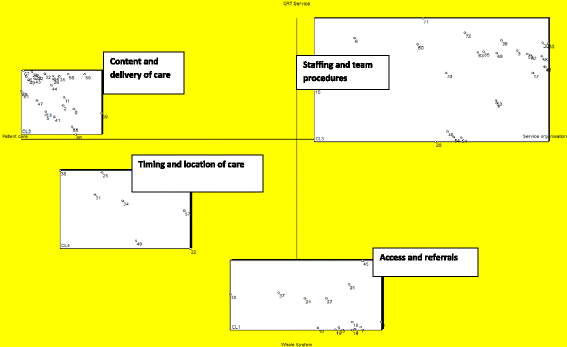
Methods: A concept mapping process was used to develop a CRT fidelity scale. Participants (n = 68) from a range of stakeholder groups prioritised and grouped statements (n = 72) about important components of the CRT model, generated from a literature review, national survey and qualitative interviews. These data were analysed using Ariadne software and the resultant cluster solution informed item selection for a CRT fidelity scale. Operational criteria and scoring anchor points were developed for each item. The CORE CRT fidelity scale was then piloted in 75 CRTs in the UK to assess the range of scores achieved and feasibility for use in a 1-day fidelity review process. Trained reviewers (n = 16) rated CRT service fidelity in a vignette exercise to test the scale's inter-rater reliability.
Results: There were high levels of agreement within and between stakeholder groups regarding the most important components of the CRT model. A 39-item measure of CRT model fidelity was developed. Piloting indicated that the scale was feasible for use to assess CRT model fidelity and had good face validity. The wide range of item scores and total scores across CRT services in the pilot demonstrate the measure can distinguish lower and higher fidelity services. Moderately good inter-rater reliability was found, with an estimated correlation between individual ratings of 0.65 (95% CI: 0.54 to 0.76).
Conclusions: The CORE CRT Fidelity Scale has been developed through a rigorous and systematic process. Promising initial testing indicates its value in assessing adherence to a model of CRT best practice and to support service improvement monitoring and planning. Further research is required to establish its psychometric properties and international applicability.
Keywords: Acute care; Crisis Resolution Team; Fidelity; Implementation; Mental health services.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials