Effect of sitagliptin on blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are treatment naive or poorly responsive to existing antidiabetic drugs: the JAMP study
- PMID: 27905912
- PMCID: PMC5133763
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-016-0149-z
Effect of sitagliptin on blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are treatment naive or poorly responsive to existing antidiabetic drugs: the JAMP study
Abstract
Background: To investigate the ameliorating effect of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, on blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were previously untreated with or who have a poor responsive to existing antidiabetic drugs.
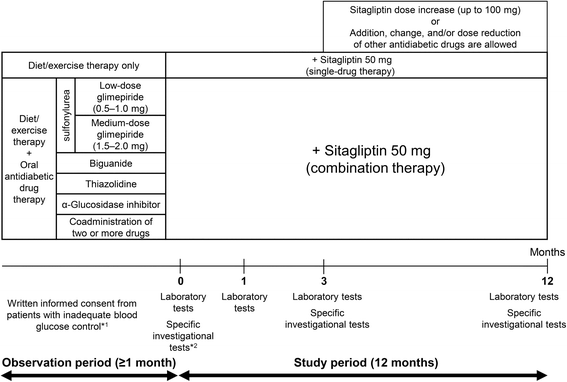
Methods: Sitagliptin (50 mg/day) was added on to the pre-existing therapy for type 2 diabetes and changes in the glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level after 3 months of treatment were compared with the baseline and performed exploratory analysis.
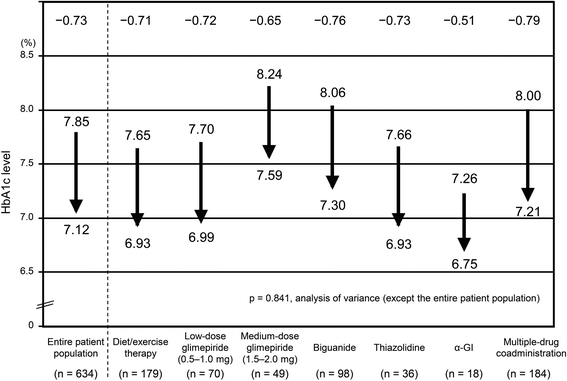
Results: HbA1c levels were significantly decreased after 1 month of treatment compared to baseline, with a mean change in HbA1c level from baseline of -0.73% (range, -0.80 to -0.67) in the entire study population at 3 months. Patients who received a medium dose of glimepiride showed the least improvement in HbA1c levels. The percentage of patients who achieved an HbA1c level of <7.0% significantly increased after 1 month of treatment, reaching 53.1% at 3 months. The percentage of patients who achieved a fasting blood glucose level of <130 mg/dL significantly increased after 1 month of treatment, reaching 50.9% at 3 months.
Conclusions: Sitagliptin improved the HbA1c level and rate of achieving the target control levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were previously untreated with, or poorly responsive to, existing antidiabetic drugs. Thus, sitagliptin is expected to be useful in this patient group. However, the additional administration of sitagliptin in patients treated with medium-dose glimepiride only slightly improved blood glucose control when corrected for baseline HbA1c level.
Keywords: DPP-4 inhibitor; Diabetes mellitus; Glimepiride; HbA1c; Sitagliptin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum level of soluble CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) predicts the response to sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes controlled inadequately by metformin and/or sulfonylurea.Transl Res. 2012 Jan;159(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22153807
-
Glimepiride strongly enhances the glucose-lowering effect in triple oral antidiabetes therapy with sitagliptin and metformin for Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013 Apr;15(4):335-41. doi: 10.1089/dia.2012.0287. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23480592 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Tolerability of Sitagliptin Compared with Glimepiride in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Inadequate Glycemic Control: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Non-Inferiority Trial.Drugs Aging. 2015 Jun;32(6):469-76. doi: 10.1007/s40266-015-0271-z. Drugs Aging. 2015. PMID: 26041585 Clinical Trial.
-
SODIUM GLUCOSE COTRANSPORTER 2 AND DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITION: PROMISE OF A DYNAMIC DUO.Endocr Pract. 2017 Jul;23(7):831-840. doi: 10.4158/EP161725.RA. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Endocr Pract. 2017. PMID: 28332871 Review.
-
Exploring the Role of Sitagliptin in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus for the Elderly: A Narrative Review.J Assoc Physicians India. 2025 Apr;73(4):e26-e32. doi: 10.59556/japi.73.0922. J Assoc Physicians India. 2025. PMID: 40200620 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors involved in decreasing the therapeutic effect of sitagliptin: a subanalysis of the JAMP study.Diabetol Int. 2017 Dec 16;9(3):158-167. doi: 10.1007/s13340-017-0340-0. eCollection 2018 Jul. Diabetol Int. 2017. PMID: 30603363 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of imeglimin-inspired novel 1,3,5-triazine derivatives as antidiabetic agents in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in Wistar rats via inhibition of DPP-4.RSC Med Chem. 2023 May 24;14(8):1512-1536. doi: 10.1039/d3md00085k. eCollection 2023 Aug 16. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37593577 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and comparison of hypoglycemic action of concomitant medications: a subanalysis of the JAMP study.Diabetol Int. 2017 Jul 28;9(1):56-65. doi: 10.1007/s13340-017-0330-2. eCollection 2018 Feb. Diabetol Int. 2017. PMID: 30603350 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Function During an Open-Label Prospective Observational Trial of Sitagliptin in Patients With Diabetes: A Sub-Analysis of the JAMP Study.J Clin Med Res. 2018 Jan;10(1):32-40. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3225w. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Clin Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29238432 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and its use in the management of metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive review on drug repositioning.Daru. 2019 Jun;27(1):341-360. doi: 10.1007/s40199-019-00238-7. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Daru. 2019. PMID: 30674032 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Results of “National Health and Nutrition Survey” . Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. 2012.
-
- Charbonnel B, Karasik A, Liu J, Wu M, Meininger G. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2638–43. doi: 10.2337/dc06-0706. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosenstock J, Brazg R, Andryuk PJ, Lu K, Stein P. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing pioglitazone therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Clin Ther. 2006;28:1556–68. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.10.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

