Trio, a Rho Family GEF, Interacts with the Presynaptic Active Zone Proteins Piccolo and Bassoon
- PMID: 27907191
- PMCID: PMC5132261
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167535
Trio, a Rho Family GEF, Interacts with the Presynaptic Active Zone Proteins Piccolo and Bassoon
Abstract
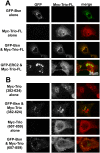
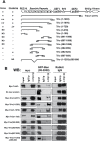
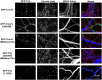
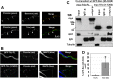
Synaptic vesicles (SVs) fuse with the plasma membrane at a precise location called the presynaptic active zone (AZ). This fusion is coordinated by proteins embedded within a cytoskeletal matrix assembled at the AZ (CAZ). In the present study, we have identified a novel binding partner for the CAZ proteins Piccolo and Bassoon. This interacting protein, Trio, is a member of the Dbl family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) known to regulate the dynamic assembly of actin and growth factor dependent axon guidance and synaptic growth. Trio was found to interact with the C-terminal PBH 9/10 domains of Piccolo and Bassoon via its own N-terminal Spectrin repeats, a domain that is also critical for its localization to the CAZ. Moreover, our data suggest that regions within the C-terminus of Trio negatively regulate its interactions with Piccolo/Bassoon. These findings provide a mechanism for the presynaptic targeting of Trio and support a model in which Piccolo and Bassoon play a role in regulating neurotransmission through interactions with proteins, including Trio, that modulate the dynamic assembly of F-actin during cycles of synaptic vesicle exo- and endocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The presynaptic scaffolding protein Piccolo organizes the readily releasable pool at the calyx of Held.J Physiol. 2018 Apr 15;596(8):1485-1499. doi: 10.1113/JP274885. Epub 2018 Jan 4. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29194628 Free PMC article.
-
Piccolo Directs Activity Dependent F-Actin Assembly from Presynaptic Active Zones via Daam1.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 21;10(4):e0120093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120093. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25897839 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-related redistribution of presynaptic proteins at the active zone.Neuroscience. 2006 Sep 1;141(3):1217-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.04.061. Epub 2006 Jun 6. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16757121
-
Molecular organization and assembly of the presynaptic active zone of neurotransmitter release.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;43:49-68. doi: 10.1007/400_012. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 17068967 Review.
-
Molecular organization of the presynaptic active zone.Cell Tissue Res. 2006 Nov;326(2):379-91. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0244-y. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Cell Tissue Res. 2006. PMID: 16865347 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of PTPσ-Mediated Presynaptic Differentiation.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019 May 22;11:17. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00017. eCollection 2019. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31191292 Free PMC article.
-
Autoinhibition of the GEF activity of cytoskeletal regulatory protein Trio is disrupted in neurodevelopmental disorder-related genetic variants.J Biol Chem. 2022 Sep;298(9):102361. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102361. Epub 2022 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35963430 Free PMC article.
-
The Burning Pain Transcriptome in the Mouse Primary Somatosensory Cortex.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 9;26(8):3538. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083538. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332032 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role for Piccolo in synaptic vesicle retrieval.Elife. 2019 May 10;8:e46629. doi: 10.7554/eLife.46629. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31074746 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinerol (CBNR) Influences Synaptic Genes Associated with Cytoskeleton and Ion Channels in NSC-34 Cell Line: A Transcriptomic Study.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 15;12(1):189. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010189. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255294 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

