Characterization and Immunomodulatory Effects of Canine Adipose Tissue- and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
- PMID: 27907211
- PMCID: PMC5131977
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167442
Characterization and Immunomodulatory Effects of Canine Adipose Tissue- and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Abstract
Background: Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) hold promise for both cell replacement and immune modulation strategies owing to their progenitor and non-progenitor functions, respectively. Characterization of MSC from different sources is an important and necessary step before clinical use of these cells is widely adopted. Little is known about the biology and function of canine MSC compared to their mouse or human counterparts. This knowledge-gap impedes development of canine evidence-based MSC technologies.
Hypothesis and objectives: We hypothesized that canine adipose tissue (AT) and bone marrow (BM) MSC (derived from the same dogs) will have similar differentiation and immune modulatory profiles. Our objectives were to evaluate progenitor and non-progenitor functions as well as other characteristics of AT- and BM-MSC including 1) proliferation rate, 2) cell surface marker expression, 3) DNA methylation levels, 4) potential for trilineage differentiation towards osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic cell fates, and 5) immunomodulatory potency in vitro.
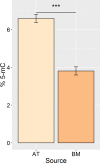
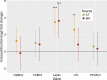
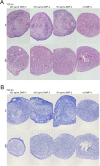
Results: 1) AT-MSC proliferated at more than double the rate of BM-MSC (population doubling times in days) for passage (P) 2, AT: 1.69, BM: 3.81; P3, AT: 1.80, BM: 4.06; P4, AT: 2.37, BM: 5.34; P5, AT: 3.20, BM: 7.21). 2) Canine MSC, regardless of source, strongly expressed cell surface markers MHC I, CD29, CD44, and CD90, and were negative for MHC II and CD45. They also showed moderate expression of CD8 and CD73 and mild expression of CD14. Minor differences were found in expression of CD4 and CD34. 3) Global DNA methylation levels were significantly lower in BM-MSC compared to AT-MSC. 4) Little difference was found between AT- and BM-MSC in their potential for adipogenesis and osteogenesis. Chondrogenesis was poor to absent for both sources in spite of adding varying levels of bone-morphogenic protein to our standard transforming growth factor (TGF-β3)-based induction medium. 5) Immunomodulatory capacity was equal regardless of cell source when tested in mitogen-stimulated lymphocyte reactions. Priming of MSC with pro-inflammatory factors interferon-gamma and/or tumour necrosis factor did not increase the lymphocyte suppressive properties of the MSC compared to untreated MSC.
Conclusions/significance: No significant differences were found between AT- and BM-MSC with regard to their immunophenotype, progenitor, and non-progenitor functions. Both MSC populations showed strong adipogenic and osteogenic potential and poor chondrogenic potential. Both significantly suppressed stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The most significant differences found were the higher isolation success and proliferation rate of AT-MSC, which could be realized as notable benefits of their use over BM-MSC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- de Bakker E, Van Ryssen B, De Schauwer C, Meyer E. Canine mesenchymal stem cells: state of the art, perspectives as therapy for dogs and as a model for man. Vet Q. 2014. January 10;2176(December 2014):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Bertolo A, Steffen F, Malonzo-Marty C, Stoyanov J. Canine Mesenchymal Stem Cell Potential and the Importance of Dog Breed—Implication for Cell-based Therapies. Cell Transplant. 2014. November 5;24(14):1969–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

