Physical activity and sedentary time in relation to academic achievement in children
- PMID: 27908560
- PMCID: PMC5429389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsams.2016.11.003
Physical activity and sedentary time in relation to academic achievement in children
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the independent and combined associations of objectively measured moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) and sedentary time (ST) with reading and arithmetic skills.
Design: Cross-sectional/prospective.
Methods: Participants were 89 boys and 69 girls aged 6-8 years. MVPA and ST were measured using a combined heart rate and movement sensor and body fat percentage by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in Grade 1. Reading fluency, reading comprehension, and arithmetic skills were assessed using standardized tests in Grades 1-3. The data were analyzed using linear regression analyses and analyses of covariance with repeated measures.
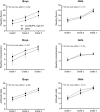
Results: In boys, MVPA was directly and ST inversely associated with reading fluency in Grades 1-3 and arithmetic skills in Grade 1 (P<0.05). Higher levels of MVPA were also related to better reading comprehension in Grade 1 (P<0.05). Most of the associations of MVPA and ST with reading and arithmetic skills attenuated after mutual adjustment for MVPA or ST. Furthermore, boys with a combination of lower levels of MVPA and higher levels of ST had consistently poorer reading fluency (P=0.002) and reading comprehension (P=0.027) across Grades 1-3 than other boys. In girls, ST was directly associated with arithmetic skills in Grade 2 (P<0.05). However, this relationship of ST with arithmetic skills was no longer significant after adjustment for body fat percentage.
Conclusions: Lower levels of MVPA and higher levels of ST and particularly their combination were related to poorer reading skills in boys. In girls, higher levels of ST were related to better arithmetic skills.
Keywords: Academic performance; Cognition; Motor activity; Pediatrics; Sedentary behavior.
Copyright © 2016 Sports Medicine Australia. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Voss M.W., Carr L.J., Clark R. Revenge of the sit II: does lifestyle impact neuronal and cognitive health through distinct mechanisms associated with sedentary behavior and physical activity? Mental Health Phys Activity. 2014;7(1):9–24.
-
- Syväoja H.J., Kantomaa M.T., Ahonen T. Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and academic performance in Finnish children. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45(11):2098–2104. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

