An anti-CD3/anti-CLL-1 bispecific antibody for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 27908880
- PMCID: PMC5290988
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-735365
An anti-CD3/anti-CLL-1 bispecific antibody for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
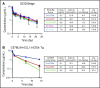
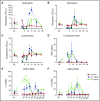
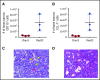
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a major unmet medical need. Most patients have poor long-term survival, and treatment has not significantly changed in 40 years. Recently, bispecific antibodies that redirect the cytotoxic activity of effector T cells by binding to CD3, the signaling component of the T-cell receptor, and a tumor target have shown clinical activity. Notably, blinatumomab is approved to treat relapsed/refractory acute lymphoid leukemia. Here we describe the design, discovery, pharmacologic activity, pharmacokinetics, and safety of a CD3 T cell-dependent bispecific (TDB) full-length human IgG1 therapeutic antibody targeting CLL-1 that could potentially be used in humans to treat AML. CLL-1 is prevalent in AML and, unlike other targets such as CD33 and CD123, is not expressed on hematopoietic stem cells providing potential hematopoietic recovery. We selected a high-affinity monkey cross-reactive anti-CLL-1 arm and tested several anti-CD3 arms that varied in affinity, and determined that the high-affinity CD3 arms were up to 100-fold more potent in vitro. However, in mouse models, the efficacy differences were less pronounced, probably because of prolonged exposure to TDB found with lower-affinity CD3 TDBs. In monkeys, assessment of safety and target cell depletion by the high- and low-affinity TDBs revealed that only the low-affinity CD3/CLL1 TDB was well tolerated and able to deplete target cells. Our data suggest that an appropriately engineered CLL-1 TDB could be effective in the treatment of AML.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures



References
-
- Freireich EJ, Wiernik PH, Steensma DP. The leukemias: a half-century of discovery. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(31):3463-3469. - PubMed
-
- Topp MS, Gökbuget N, Zugmaier G, et al. . Long-term follow-up of hematologic relapse-free survival in a phase 2 study of blinatumomab in patients with MRD in B-lineage ALL. Blood. 2012;120(26):5185-5187. - PubMed
-
- Topp MS, Kufer P, Gökbuget N, et al. . Targeted therapy with the T-cell-engaging antibody blinatumomab of chemotherapy-refractory minimal residual disease in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients results in high response rate and prolonged leukemia-free survival. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(18):2493-2498. - PubMed
-
- Kung Sutherland MS, Walter RB, Jeffrey SC, et al. . SGN-CD33A: a novel CD33-targeting antibody-drug conjugate using a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer is active in models of drug-resistant AML. Blood. 2013;122(8):1455-1463. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

