Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation After Catheter Ablation: Considerations For Repeat Ablation And Strategies To Optimize Success
- PMID: 27909521
- PMCID: PMC5089515
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.1427
Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation After Catheter Ablation: Considerations For Repeat Ablation And Strategies To Optimize Success
Abstract
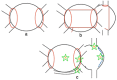
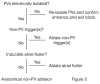
Recurrent AF after catheter ablation occurs in at least 20 to 40% of patients. Repeat ablation is primarily considered for those with symptomatic AF recurrences (often drug-refactory) occurring at least 3 months or more post-ablation. Pulmonary vein reconnection is almost universally encountered, and repeat isolation of electrically connected pulmonary veins should be the primary ablation strategy. Beyond repeat PVI and possible ablation of non-PV triggers, there is little to no evidence that additional substrate modification improves outcomes. In addition to repeat ablation, it is critical to address and treat comorbid conditions which increase arrhythmia risk post-ablation. Specifically, obesity, hypertension, and sleep-disordered breathing should be targeted and modified to increase the likelihood of success.
Keywords: Atrial Fibrillation Ablation; Atrial Fibrillation Lifestyle Modification; Pulmonary Vein Reconnection; Repeat Catheter Ablation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Catheter Ablation of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Have We Achieved Cure with Pulmonary Vein Isolation?Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2015 Apr-Jun;11(2):71-5. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-11-2-71. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2015. PMID: 26306122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Ablation Index-Guided Ablation Results in High Rates of Durable Pulmonary Vein Isolation and Freedom From Arrhythmia in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Patients: The PRAISE Study Results.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2018 Sep;11(9):e006576. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.118.006576. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2018. PMID: 30354288
-
Atrial fibrillation patients with isolated pulmonary veins: Is sinus rhythm achievable?J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017 Jul;28(7):754-761. doi: 10.1111/jce.13230. Epub 2017 Jun 23. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28429499
-
Pulmonary vein reconnection and arrhythmia progression after antral linear catheter ablation of paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation.Clin Res Cardiol. 2016 Sep;105(9):738-43. doi: 10.1007/s00392-016-0980-2. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Clin Res Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27048420
-
[Interventional therapy of atrial fibrillation: possibilities and limitations].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2010 Mar;135 Suppl 2:S48-54. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1249209. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2010. PMID: 20221979 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Recurrent atrial fibrillation/flutter detection after ablation or cardioversion using the AliveCor KardiaMobile device: iHEART results.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019 Nov;30(11):2220-2228. doi: 10.1111/jce.14160. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31507001 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The higher recurrence rate after catheter ablation in younger patients with atrial fibrillation suggesting different pathophysiology.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2023 Oct;66(7):1609-1619. doi: 10.1007/s10840-022-01461-0. Epub 2023 Jan 17. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2023. PMID: 36648614
-
Association between specific antiarrhythmic drug prescription in the post-procedural blanking period and recurrent atrial arrhythmias after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 24;16(6):e0253266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253266. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34166392 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Outcomes and Predictors of Late Recurrence in Young Patients with Atrial Fibrillation after Catheter Ablation.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 May 29;2023:7892185. doi: 10.1155/2023/7892185. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37284170 Free PMC article.
-
Catheter ablation in grown-up congenital heart disease patients: A single-center experience.Int J Cardiol Congenit Heart Dis. 2022 Jan 14;7:100326. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcchd.2022.100326. eCollection 2022 Mar. Int J Cardiol Congenit Heart Dis. 2022. PMID: 39712280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calkins Hugh, Kuck Karl Heinz, Cappato Riccardo, Brugada Josep, Camm A John, Chen Shih-Ann, Crijns Harry J G, Damiano Ralph J, Davies D Wyn, DiMarco John, Edgerton James, Ellenbogen Kenneth, Ezekowitz Michael D, Haines David E, Haissaguerre Michel, Hindricks Gerhard, Iesaka Yoshito, Jackman Warren, Jalife Jose, Jais Pierre, Kalman Jonathan, Keane David, Kim Young-Hoon, Kirchhof Paulus, Klein George, Kottkamp Hans, Kumagai Koichiro, Lindsay Bruce D, Mansour Moussa, Marchlinski Francis E, McCarthy Patrick M, Mont J Lluis, Morady Fred, Nademanee Koonlawee, Nakagawa Hiroshi, Natale Andrea, Nattel Stanley, Packer Douglas L, Pappone Carlo, Prystowsky Eric, Raviele Antonio, Reddy Vivek, Ruskin Jeremy N, Shemin Richard J, Tsao Hsuan-Ming, Wilber David. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. Europace. 2012 Apr;14 (4):528–606. - PubMed
-
- Pappone Carlo, Augello Giuseppe, Sala Simone, Gugliotta Filippo, Vicedomini Gabriele, Gulletta Simone, Paglino Gabriele, Mazzone Patrizio, Sora Nicoleta, Greiss Isabelle, Santagostino Andreina, LiVolsi Laura, Pappone Nicola, Radinovic Andrea, Manguso Francesco, Santinelli Vincenzo. A randomized trial of circumferential pulmonary vein ablation versus antiarrhythmic drug therapy in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the APAF Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006 Dec 5;48 (11):2340–7. - PubMed
-
- Wazni Oussama M, Marrouche Nassir F, Martin David O, Verma Atul, Bhargava Mandeep, Saliba Walid, Bash Dianna, Schweikert Robert, Brachmann Johannes, Gunther Jens, Gutleben Klaus, Pisano Ennio, Potenza Dominico, Fanelli Raffaele, Raviele Antonio, Themistoclakis Sakis, Rossillo Antonio, Bonso Aldo, Natale Andrea. Radiofrequency ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of symptomatic atrial fibrillation: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2005 Jun 1;293 (21):2634–40. - PubMed
-
- Jaïs Pierre, Cauchemez Bruno, Macle Laurent, Daoud Emile, Khairy Paul, Subbiah Rajesh, Hocini Mélèze, Extramiana Fabrice, Sacher Fréderic, Bordachar Pierre, Klein George, Weerasooriya Rukshen, Clémenty Jacques, Haïssaguerre Michel. Catheter ablation versus antiarrhythmic drugs for atrial fibrillation: the A4 study. Circulation. 2008 Dec 9;118 (24):2498–505. - PubMed
-
- Oral Hakan, Pappone Carlo, Chugh Aman, Good Eric, Bogun Frank, Pelosi Frank, Bates Eric R, Lehmann Michael H, Vicedomini Gabriele, Augello Giuseppe, Agricola Eustachio, Sala Simone, Santinelli Vincenzo, Morady Fred. Circumferential pulmonary-vein ablation for chronic atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006 Mar 2;354 (9):934–41. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
