AAV-mediated Sirt1 overexpression in skeletal muscle activates oxidative capacity but does not prevent insulin resistance
- PMID: 27909699
- PMCID: PMC5111573
- DOI: 10.1038/mtm.2016.72
AAV-mediated Sirt1 overexpression in skeletal muscle activates oxidative capacity but does not prevent insulin resistance
Abstract
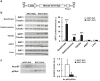
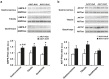
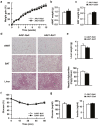
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by triglyceride accumulation and reduced lipid oxidation capacity in skeletal muscle. SIRT1 is a key protein in the regulation of lipid oxidation and its expression is reduced in the skeletal muscle of insulin resistant mice. In this tissue, Sirt1 up-regulates the expression of genes involved in oxidative metabolism and improves mitochondrial function mainly through PPARGC1 deacetylation. Here we examined whether Sirt1 overexpression mediated by adeno-associated viral vectors of serotype 1 (AAV1) specifically in skeletal muscle can counteract the development of insulin resistance induced by a high fat diet in mice. AAV1-Sirt1-treated mice showed up-regulated expression of key genes related to β-oxidation together with increased levels of phosphorylated AMP protein kinase. Moreover, SIRT1 overexpression in skeletal muscle also increased basal phosphorylated levels of AKT. However, AAV1-Sirt1 treatment was not enough to prevent high fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Although Sirt1 gene transfer to skeletal muscle induced changes at the muscular level related with lipid and glucose homeostasis, our data indicate that overexpression of SIRT1 in skeletal muscle is not enough to improve whole-body insulin resistance and that suggests that SIRT1 has to be increased in other metabolic tissues to prevent insulin resistance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
AAV8-mediated Sirt1 gene transfer to the liver prevents high carbohydrate diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2014 Oct 1;1:14039. doi: 10.1038/mtm.2014.39. eCollection 2014. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2014. PMID: 26015978 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle-specific overexpression of heat shock protein 72 improves skeletal muscle insulin-stimulated glucose uptake but does not alter whole body metabolism.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Aug;20(8):1928-1936. doi: 10.1111/dom.13319. Epub 2018 May 3. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29652108
-
SIRT1 attenuates high glucose-induced insulin resistance via reducing mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 May;240(5):557-65. doi: 10.1177/1535370214557218. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25710929 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of SIRT1 in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Jan 16;69:63-8. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1136379. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 25614674 Review. Polish.
-
SIRT1 and insulin resistance.J Diabetes Complications. 2016 Jan-Feb;30(1):178-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.08.022. Epub 2015 Sep 2. J Diabetes Complications. 2016. PMID: 26422395 Review.
Cited by
-
Eternal Youth: A Comprehensive Exploration of Gene, Cellular, and Pharmacological Anti-Aging Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 4;25(1):643. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010643. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Obesity to Hippocampal Neurodegeneration: Pathogenesis and Non-Pharmacological Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 28;22(1):201. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010201. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33379163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Histone Deacetylases in Skeletal Muscle Physiology and Systemic Energy Homeostasis: Implications for Metabolic Diseases and Therapy.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 11;11:949. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00949. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32848876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-Specific PEGylated Adeno-Associated Viruses with Increased Serum Stability and Reduced Immunogenicity.Molecules. 2017 Jul 11;22(7):1155. doi: 10.3390/molecules22071155. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28696391 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal gating of SIRT1 functions by O-GlcNAcylation is essential for liver metabolic switching and prevents hyperglycemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Mar 24;117(12):6890-6900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1909943117. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32152092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen, L, Magliano, DJ and Zimmet, PZ (2011). The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus–present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8: 228–236. - PubMed
-
- Schrauwen, P (2007). High-fat diet, muscular lipotoxicity and insulin resistance. Proc Nutr Soc 66: 33–41. - PubMed
-
- Sun, C, Zhang, F, Ge, X, Yan, T, Chen, X, Shi, X et al. (2007). SIRT1 improves insulin sensitivity under insulin-resistant conditions by repressing PTP1B. Cell Metab 6: 307–319. - PubMed
-
- Sesti, G (2006). Pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 20: 665–679. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

