The Inventory of Callous-Unemotional Traits (ICU) in Children: Reliability and Heritability
- PMID: 27909830
- PMCID: PMC5305430
- DOI: 10.1007/s10519-016-9831-1
The Inventory of Callous-Unemotional Traits (ICU) in Children: Reliability and Heritability
Abstract
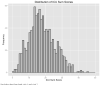
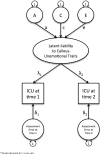
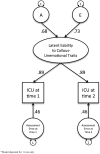
Callous-unemotional (CU) traits comprise the core symptoms of psychopathy, yet no study has estimated the heritability of CU traits in a community sample of children using an instrument designed solely to assess CU traits. The current study uses data from 339 twin pairs aged 9-14 to examine the reliability and heritability of the parent-report Inventory of Callous-unemotional Traits (ICU) at two assessments approximately 3 weeks apart. Time-specific measurement error was taken into account to obtain a more accurate estimate of the heritability reflecting the latent liability to CU traits. Test-retest reliability was 0.84 and heritability at visit 1 was 39%. The heritability of the latent liability to CU traits was 47%. This latent liability contributed 79% of the variance in ICU score at visit 1 and visit 2. This is the first study to account for measurement error while examining the heritability of CU traits, furthering our understanding of psychopathy in children.
Keywords: Callous-unemotional traits; Heritability; Measurement model; Reliability; Twins.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3rd ed American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 1980.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2013.
-
- Bardone AM, Moffitt TE, Caspi A, Dickson N, Stanton WR, Silva PA. Adult physical health outcomes of adolescent girls with conduct disorder, depression, and anxiety. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998;37(6):594–601. - PubMed
-
- Barker C, Pistrang N, Elliott R. Research methods in clinical and counseling psychology. John Wiley; Chichester: 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical