Paper-based CRP Monitoring Devices
- PMID: 27910861
- PMCID: PMC5133555
- DOI: 10.1038/srep38171
Paper-based CRP Monitoring Devices
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Paper-based CRP Monitoring Devices.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 16;7:44721. doi: 10.1038/srep44721. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28300187 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
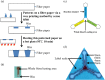
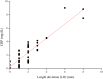
Here, we discuss the development of a paper-based diagnostic device that is inexpensive, portable, easy-to-use, robust, and capable of running simultaneous tests to monitor a relevant inflammatory protein for clinical diagnoses i.e. C-reactive protein (CRP). In this study, we first attempted to make a paper-based diagnostic device via the wax printing method, a process that was used in previous studies. This device has two distinct advantages: 1) reduced manufacturing and assay costs and operation duration via using wax printing method to define hydrophobic boundaries (for fluidic devices or general POC devices); and, 2) the hydrophilicity of filter paper, which is used to purify and chromatographically correct interference caused by whole blood components with a tiny amount of blood sample (only 5 μL). Diagnosis was based on serum stain length retained inside the paper channels of our device. This is a balanced function between surface tension and chromatographic force following immune reactions (CRP assays) with a paper-embedded biomarker.
Figures




References
-
- Gubala V., Harris L. F., Ricco A. J., Tan M. X. & Williams D. E. Point of care diagnostics: status and future. Anal. Chem. 84, 487–515 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Chin C. D., Linder V. & Sia S. K. Lab-on-a-chip devices for global health: past studies and future opportunities. Lab Chip 7, 41–57 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Sia S. K., Linder V., Parviz B. A., Siegel A. & Whitesides G. M. An integrated approach to a portable and low-cost immunoassay for resource-poor settings. Angew. Chem. 43, 498–502 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Daar A. S. et al.. Top ten biotechnologies for improving health in developing countries. Nat. Genet. 32, 229–232 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Yager P. et al.. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature 442, 412–418 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

