Family PArtners in Lifestyle Support (PALS): Family-based weight loss for African American adults with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 27911049
- PMCID: PMC5182111
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.21700
Family PArtners in Lifestyle Support (PALS): Family-based weight loss for African American adults with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To develop and test a family-centered behavioral weight loss intervention for African American adults with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: In this randomized trial, dyads consisting of an African American adult with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes (index participant) paired with a family partner with overweight or obesity but not diagnosed with diabetes were assigned in a 2:1 ratio to a 20-week special intervention (SI) or delayed intervention (DI) control group. The primary outcome was weight loss among index participants at the 20-week follow-up.
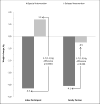
Results: One hundred eight participants (54 dyads-36 (SI) and 18 (DI) dyads) were enrolled: 81% females; mean age, 51 years; mean weight,103 kg; and mean BMI, 37 kg/m2 . At post-intervention, 96 participants (89%) returned for follow-up measures. Among index participants, mean difference in weight loss between groups was -5.0 kg, P <0.0001 (-3.6 kg loss among SI; 1.4 kg gain in DI). SI index participants showed significantly greater improvements in hemoglobin A1c, depressive symptoms, family interactions, and dietary, physical activity, and diabetes self-care behaviors. SI family partners also had significant weight loss (-3.9 kg (SI) vs. -1.0 kg (DI), P = 0.02).
Conclusions: A family-centered, behavioral weight loss intervention led to clinically significant short-term weight loss among family dyads.
© 2016 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Must A, McKeown NM. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. In: De Groot LJ, Beck-Peccoz P, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A, Hershman JM, et al., editors. Endotext. South Dartmouth, MA: MDText.com, Inc; 2000.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States, 2014. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2014.
-
- Colberg SR, Albright AL, Blissmer BJ, et al. Exercise and type 2 diabetes: American College of Sports Medicine and the American Diabetes Association: joint position statement. Exercise and type 2 diabetes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42:2282–2303. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

