KLB is associated with alcohol drinking, and its gene product β-Klotho is necessary for FGF21 regulation of alcohol preference
- PMID: 27911795
- PMCID: PMC5167198
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1611243113
KLB is associated with alcohol drinking, and its gene product β-Klotho is necessary for FGF21 regulation of alcohol preference
Abstract
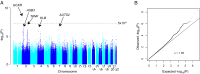
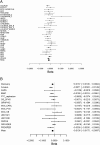
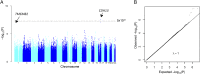
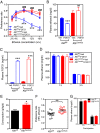
Excessive alcohol consumption is a major public health problem worldwide. Although drinking habits are known to be inherited, few genes have been identified that are robustly linked to alcohol drinking. We conducted a genome-wide association metaanalysis and replication study among >105,000 individuals of European ancestry and identified β-Klotho (KLB) as a locus associated with alcohol consumption (rs11940694; P = 9.2 × 10-12). β-Klotho is an obligate coreceptor for the hormone FGF21, which is secreted from the liver and implicated in macronutrient preference in humans. We show that brain-specific β-Klotho KO mice have an increased alcohol preference and that FGF21 inhibits alcohol drinking by acting on the brain. These data suggest that a liver-brain endocrine axis may play an important role in the regulation of alcohol drinking behavior and provide a unique pharmacologic target for reducing alcohol consumption.
Keywords: FGF21; alcohol consumption; human; mouse model; β-Klotho.
Conflict of interest statement
B. Psaty serves on the Data and Safety Monitoring Board for a clinical trial funded by the manufacturer (Zoll LifeCor) and the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access project funded by Johnson & Johnson. D.J.M. serves on the scientific advisory board of Metacrine. The other authors report no competing financial interests.
Figures

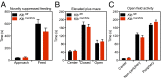
References
-
- Anonymous . Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health. WHO; Geneva: 2014.
-
- Rehm J, et al. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet. 2009;373(9682):2223–2233. - PubMed
-
- Heath AC, Meyer J, Eaves LJ, Martin NG. The inheritance of alcohol consumption patterns in a general population twin sample. I. Multidimensional scaling of quantity/frequency data. J Stud Alcohol. 1991;52(4):345–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N015746/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01632X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01341X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CZD/16/6/4/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

