Relative Contributions of Arterial Stiffness and Hypertension to Cardiovascular Disease: The Framingham Heart Study
- PMID: 27912210
- PMCID: PMC5210358
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004271
Relative Contributions of Arterial Stiffness and Hypertension to Cardiovascular Disease: The Framingham Heart Study
Abstract
Background: The presence and implications of abnormal arterial stiffness, a potential independent predictor of outcomes, in community-dwelling treated hypertensives is unknown. Furthermore, limited data exist regarding the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) associated with arterial stiffness across the entire range of blood pressure.
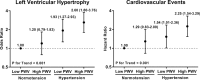
Methods and results: We measured carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) and classical CVD risk factors in 2127 community-dwelling participants (mean age 60 years, 57% women) of The Framingham Offspring Cohort. The participants were divided into 4 groups according to hypertension (yes/no, defined as blood pressure ≥140/90 mm Hg or use of antihypertensive treatment) and PWV status (high/low based on age- and sex-specific median values) and followed up for CVD events (CVD death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, heart failure, and stroke). Sixty percent (233 of 390) of controlled and 90% (232 of 258) of uncontrolled treated hypertensives had high PWV. The multivariable-adjusted risk for CVD events (n=248, median follow-up 12.6 years) rose from normotension with low PWV (reference) to normotension with high PWV (hazard ratio 1.29, 95% CI 0.83-2.00) and from hypertension with low PWV (hazard ratio 1.54, 95% CI 1.01-2.36) to hypertension with high PWV (hazard ratio 2.25, 95% CI 1.54-3.29).
Conclusions: A substantial proportion of treated hypertensives have high arterial stiffness, a finding that may explain some of the notable residual CVD risk associated with even well-controlled hypertension. High PWV is associated with a trend towards increasing CVD risk in both nonhypertensives and hypertensives, a finding that may support the use of arterial stiffness measurements in both populations.
Keywords: antihypertensive agent; arterial stiffness; cardiovascular disease; epidemiology; hypertension.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


References
-
- Chow CK, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, Islam S, Gupta R, Avezum A, Bahonar A, Chifamba J, Dagenais G, Diaz R, Kazmi K, Lanas F, Wei L, Lopez‐Jaramillo P, Fanghong L, Ismail NH, Puoane T, Rosengren A, Szuba A, Temizhan A, Wielgosz A, Yusuf R, Yusufali A, McKee M, Liu L, Mony P, Yusuf S; PURE (Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology) Study investigators . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high‐, middle‐, and low‐income countries. JAMA. 2013;310:959–968. - PubMed
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair‐Rohani H, Amann M, Anderson HR, Andrews KG, Aryee M, Atkinson C, Bacchus LJ, Bahalim AN, Balakrishnan K, Balmes J, Barker‐Collo S, Baxter A, Bell ML, Blore JD, Blyth F, Bonner C, Borges G, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Brauer M, Brooks P, Bruce NG, Brunekreef B, Bryan‐Hancock C, Bucello C, Buchbinder R, Bull F, Burnett RT, Byers TE, Calabria B, Carapetis J, Carnahan E, Chafe Z, Charlson F, Chen H, Chen JS, Cheng AT, Child JC, Cohen A, Colson KE, Cowie BC, Darby S, Darling S, Davis A, Degenhardt L, Dentener F, Des Jarlais DC, Devries K, Dherani M, Ding EL, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Edmond K, Ali SE, Engell RE, Erwin PJ, Fahimi S, Falder G, Farzadfar F, Ferrari A, Finucane MM, Flaxman S, Fowkes FG, Freedman G, Freeman MK, Gakidou E, Ghosh S, Giovannucci E, Gmel G, Graham K, Grainger R, Grant B, Gunnell D, Gutierrez HR, Hall W, Hoek HW, Hogan A, Hosgood HD, Hoy D, Hu H, Hubbell BJ, Hutchings SJ, Ibeanusi SE, Jacklyn GL, Jasrasaria R, Jonas JB, Kan H, Kanis JA, Kassebaum N, Kawakami N, Khang YH, Khatibzadeh S, Khoo JP, Kok C, Laden F, Lalloo R, Lan Q, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Leigh J, Li Y, Lin JK, Lipshultz SE, London S, Lozano R, Lu Y, Mak J, Malekzadeh R, Mallinger L, Marcenes W, March L, Marks R, Martin R, McGale P, McGrath J, Mehta S, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Micha R, Michaud C, Mishra V, Mohd Hanafiah K, Mokdad AA, Morawska L, Mozaffarian D, Murphy T, Naghavi M, Neal B, Nelson PK, Nolla JM, Norman R, Olives C, Omer SB, Orchard J, Osborne R, Ostro B, Page A, Pandey KD, Parry CD, Passmore E, Patra J, Pearce N, Pelizzari PM, Petzold M, Phillips MR, Pope D, Pope CA III, Powles J, Rao M, Razavi H, Rehfuess EA, Rehm JT, Ritz B, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Robinson C, Rodriguez‐Portales JA, Romieu I, Room R, Rosenfeld LC, Roy A, Rushton L, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanchez‐Riera L, Sanman E, Sapkota A, Seedat S, Shi P, Shield K, Shivakoti R, Singh GM, Sleet DA, Smith E, Smith KR, Stapelberg NJ, Steenland K, Stockl H, Stovner LJ, Straif K, Straney L, Thurston GD, Tran JH, Van Dingenen R, van Donkelaar A, Veerman JL, Vijayakumar L, Weintraub R, Weissman MM, White RA, Whiteford H, Wiersma ST, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Williams W, Wilson N, Woolf AD, Yip P, Zielinski JM, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, Ezzati M, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O'Rourke MF, Hashimoto J. Mechanical factors in arterial aging: a clinical perspective. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Safar ME, Toto‐Moukouo JJ, Bouthier JA, Asmar RE, Levenson JA, Simon AC, London GM. Arterial dynamics, cardiac hypertrophy, and antihypertensive treatment. Circulation. 1987;75:I156–I161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

