Long-term effect of stents eluting 6-mercaptopurine in porcine coronary arteries
- PMID: 27916002
- PMCID: PMC5137209
- DOI: 10.1186/s12952-016-0063-y
Long-term effect of stents eluting 6-mercaptopurine in porcine coronary arteries
Abstract
Background: Drug-eluting stents (DES) have dramatically reduced restenosis rates compared to bare metal stents and are widely used in coronary artery angioplasty. The anti-proliferative nature of the drugs reduces smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation effectively, but unfortunately also negatively affects endothelialization of stent struts, necessitating prolonged dual anti-platelet therapy. Cell-type specific therapy may prevent this complication, giving rise to safer stents that do not require additional medication. 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) is a drug with demonstrated cell-type specific effects on vascular cells both in vitro and in vivo, inhibiting proliferation of SMCs while promoting survival of endothelial cells. In rabbits, we demonstrated that DES locally releasing 6-MP during 4 weeks reduced in-stent stenosis by inhibiting SMC proliferation and reducing inflammation, without negatively affecting endothelialization of the stent surface. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether 6-MP-eluting stents are similarly effective in preventing stenosis in porcine coronary arteries after 3 months, in order to assess the eligibility for human application.
Methods: 6-MP-eluting and polymer-only control stents (both n = 7) were implanted in porcine coronary arteries after local balloon injury to assess the effect of 6-MP on vascular lesion formation. Three months after implantation, stented coronary arteries were harvested and analyzed.
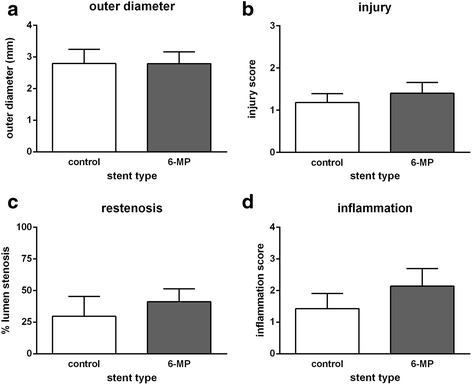
Results: Morphometric analyses revealed that stents were implanted reproducibly and with limited injury to the vessel wall. Unexpectedly, both in-stent stenosis (6-MP: 41.1 ± 10.3 %; control: 29.6 ± 5.9 %) and inflammation (6-MP: 2.14 ± 0.51; control: 1.43 ± 0.45) were similar between the groups after 3 months.
Conclusion: In conclusion, although 6-MP was previously found to potently inhibit SMC proliferation, reduce inflammation and promote endothelial cell survival, thereby effectively reducing in-stent restenosis in rabbits, stents containing 300 μg 6-MP did not reduce stenosis and inflammation in porcine coronary arteries.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stents Eluting 6-Mercaptopurine Reduce Neointima Formation and Inflammation while Enhancing Strut Coverage in Rabbits.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 21;10(9):e0138459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138459. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26389595 Free PMC article.
-
Rationale and study design of the OISTER trial: optical coherence tomography evaluation of stent struts re-endothelialization in patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes--a comparison of the intrEpide tRapidil eluting stent vs. taxus drug-eluting stent implantation.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2010 Jul;11(7):536-43. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e32833499c4. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2010. PMID: 20090547 Clinical Trial.
-
A novel CX3CR1 antagonist eluting stent reduces stenosis by targeting inflammation.Biomaterials. 2015 Nov;69:22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.07.059. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26275859
-
Drug-eluting stents.Arch Cardiol Mex. 2006 Jul-Sep;76(3):297-319. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2006. PMID: 17091802 Review.
-
Eluting combination drugs from stents.Int J Pharm. 2013 Sep 15;454(1):4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.07.005. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Int J Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23850234 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the healing process after percutaneous implantation of a cardiovascular device: a systematic review.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Mar;36(3):385-394. doi: 10.1007/s10554-019-01734-2. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31745743
-
Evolution of drug-eluting biomedical implants for sustained drug delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021 Feb;159:21-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.12.005. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021. PMID: 33338604 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- King SB, 3rd, Smith SC, Jr, Hirshfeld JW, Jr, Jacobs AK, Morrison DA, Williams DO, et al. 2007 focused update of the ACC/AHA/SCAI 2005 guideline update for percutaneous coronary intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:172–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.10.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Loh JP, Torguson R, Pendyala LK, Omar A, Chen F, Satler LF, Pichard AD, Waksman R. Impact of early versus late clopidogrel discontinuation on stent thrombosis following percutaneous coronary intervention with first- and second-generation drug-eluting stents. Am J Cardiol. 2014;113(12):1968–76. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.03.041. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

