The Relevance of Ultrasound Imaging of Suspicious Axillary Lymph Nodes and Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy in the Post-ACOSOG Z11 Era in Early Breast Cancer
- PMID: 27916595
- PMCID: PMC5309157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.10.005
The Relevance of Ultrasound Imaging of Suspicious Axillary Lymph Nodes and Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy in the Post-ACOSOG Z11 Era in Early Breast Cancer
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: Evaluation of nodal involvement in early-stage breast cancers (T1 or T2) changed following the Z11 trial; however, not all patients meet the Z11 inclusion criteria. Hence, the relevance of ultrasound imaging of the axilla and fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) in early-stage breast cancers was investigated.
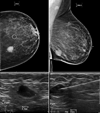
Materials and methods: In this single-center, retrospective study, 758 subjects had pathology-verified breast cancer diagnosis over a 3-year period, of which 128 subjects with T1 or T2 breast tumors had abnormal axillary lymph nodes on ultrasound, had FNA, and proceeded to axillary surgery. Ultrasound images were reviewed and analyzed using multivariable logistic regression to identify the features predictive of positive FNA. Accuracy of FNA was quantified as the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve with axillary surgery as reference standard.
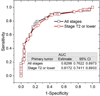
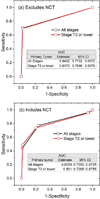
Results: Of 128 subjects, 61 were positive on FNA and 65 were positive on axillary surgery. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of FNA were 52 of 65 (80%), 54 of 63 (85.7%), 52 of 61(85.2%), and 54 of 67 (80.5%), respectively. After adjusting for neoadjuvant chemotherapy between FNA and surgery, a positive FNA was associated with higher likelihood for positive axillary surgery (odds ratio: 22.7; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 7.2-71.3, P < .0001), and the accuracy of FNA was 0.801 (95% CI: 0.727-0.876). Among ultrasound imaging features, cortical thickness and abnormal hilum were predictive (P < .017) of positive FNA with accuracy of 0.817 (95% CI: 0.741-0.893).
Conclusions: Ultrasound imaging and FNA can play an important role in the management of early breast cancers even in the post-Z11 era. Higher weightage can be accorded to cortical thickness and hilum during ultrasound evaluation.
Keywords: Breast cancer; axilla; axillary lymph node dissection; fine-needle aspiration; lymph node; sentinel node biopsy; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2017 The Association of University Radiologists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Axillary Staging of Early-Stage Invasive Breast Cancer by Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology: Which Ultrasound Criteria for Classifying Abnormal Lymph Nodes Should Be Adopted in the Post-ACOSOG Z0011 Trial Era?J Ultrasound Med. 2016 May;35(5):885-93. doi: 10.7863/ultra.15.06019. Epub 2016 Mar 23. J Ultrasound Med. 2016. PMID: 27009312
-
Impact of sentinel lymph node biopsy by ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy for patients with suspicious node positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2018 Jan;25(1):86-93. doi: 10.1007/s12282-017-0795-7. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28735457
-
Nonimage-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy of palpable axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients.Breast J. 2012 Jan-Feb;18(1):3-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2011.01180.x. Epub 2011 Nov 20. Breast J. 2012. PMID: 22098412
-
Meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy in diagnosing axillary lymph node metastasis.Br J Surg. 2018 Sep;105(10):1244-1253. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10920. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Br J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29972239
-
Performance characteristics of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of axillary lymph nodes for metastatic breast cancer employing rapid on-site evaluation of adequacy: analysis of 136 cases and review of the literature.Cancer Cytopathol. 2014 Apr;122(4):282-91. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21384. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014. PMID: 24353146 Review.
Cited by
-
Noninvasive prediction of node-positive breast cancer response to presurgical neoadjuvant chemotherapy therapy based on machine learning of axillary lymph node ultrasound.J Transl Med. 2023 May 21;21(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04201-8. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37211604 Free PMC article.
-
Unifocal Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: Tumor Size Concordance Between Preoperative Ultrasound Imaging and Postoperative Pathology.Clin Breast Cancer. 2018 Dec;18(6):e1367-e1372. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Clin Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30131246 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Axillary ultrasonography combined with pre-operative wire localisation of clipped node in nodal restaging after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in node positive breast cancer patients: a pilot study.Br J Radiol. 2021 Nov 1;94(1127):20210788. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210788. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34491822 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound guided needle biopsy of axilla to evaluate nodal metastasis after preoperative systemic therapy in cohort of 106 breast cancers enriched with BRCA1/2 pathogenic variant carriers.Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2021 Jul 7;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13053-021-00187-w. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34233740 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Imaging Morphology is Associated with Biological Behavior in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast.J Clin Imaging Sci. 2021 Sep 2;11:48. doi: 10.25259/JCIS_60_2021. eCollection 2021. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2021. PMID: 34513212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rivadeneira DE, Simmons RM, Christos PJ, Hanna K, Daly JM, Osborne MP. Predictive factors associated with axillary lymph node metastases in T1a and T1b breast carcinomas: analysis in more than 900 patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;191(1):1–6. discussion -8. - PubMed
-
- Hieken TJ, Trull BC, Boughey JC, et al. Preoperative axillary imaging with percutaneous lymph node biopsy is valuable in the contemporary management of patients with breast cancer. Surgery. 2013;154(4):831–838. discussion 8–40. - PubMed
-
- Cools-Lartigue J, Sinclair A, Trabulsi N, et al. Preoperative axillary ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis of axillary metastases in patients with breast cancer: predictors of accuracy and future implications. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(3):819–827. - PubMed
-
- Koelliker SL, Chung MA, Mainiero MB, Steinhoff MM, Cady B. Axillary lymph nodes: US-guided fine-needle aspiration for initial staging of breast cancer--correlation with primary tumor size. Radiology. 2008;246(1):81–89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

