Impact of Sequencing Targeted Therapies With High-dose Interleukin-2 Immunotherapy: An Analysis of Outcome and Survival of Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma From an On-going Observational IL-2 Clinical Trial: PROCLAIMSM
- PMID: 27916626
- PMCID: PMC6875755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clgc.2016.10.008
Impact of Sequencing Targeted Therapies With High-dose Interleukin-2 Immunotherapy: An Analysis of Outcome and Survival of Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma From an On-going Observational IL-2 Clinical Trial: PROCLAIMSM
Abstract
Background: This analysis describes the outcome for patients who received targeted therapy (TT) prior to or following high-dose interleukin-2 (HD IL-2).
Patients and methods: Patients with renal cell carcinoma (n = 352) receiving HD IL-2 were enrolled in ProleukinR Observational Study to Evaluate the Treatment Patterns and Clinical Response in Malignancy (PROCLAIMSM) beginning in 2011. Statistical analyses were performed using datasets as of September 24, 2015.
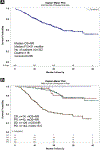
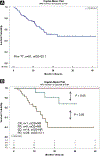
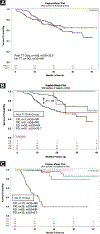
Results: Overall, there were 4% complete response (CR), 13% partial response (PR), 39% stable disease (SD), and 43% progressive disease (PD) with HD IL-2. The median overall survival (mOS) was not reached in patients with CR, PR, or SD, and was 15.5 months in patients with PD (median follow-up, 21 months). Sixty-one patients had prior TT before HD IL-2 with an overall response rate (ORR) to HD IL-2 of 19% (1 CR, 9 PR) and an mOS of 22.1 months. One hundred forty-nine patients received TT only after HD IL-2 with an mOS of 35.5 months. One hundred forty-two patients had no TT before or after HD IL-2, and mOS was not reached. The mOS was 8.5 months in PD patients who received HD IL-2 without follow-on TT and 29.7 months in PD patients who received follow-on TT after HD IL-2.
Conclusions: HD IL-2 as sole front-line therapy, in the absence of added TT, shows extended clinical benefit (CR, PR, and SD). Patients with PD after HD IL-2 appear to benefit from follow-on TT. Patients who progressed on TT and received follow-on HD IL-2 experienced major clinical benefit. HD IL-2 therapy should be considered in eligible patients.
Keywords: Anti-VEGF therapy; Cytokine; Kidney cancer; Therapy trends; Toxicity.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
Dr Amin Asim reports Speakers’ Bureau support from BMS, Merck, and Pfizer; Dr Brendan D. Curti reports travel, accommodations, and expenses support from Agonox, BMS, and Prometheus; research funding from Prometheus and Galectin Therapeutics; honoraria from Prometheus Laboratories Inc; Speakers’ Bureau support from Prometheus; and is also an unpaid consultant for Agonox and Ubivac; Dr Bret Taback reports Speakers’ Bureau support from Prometheus; Dr David F. McDermott has performed in a consulting or advisory role for Merck, Genentech, Novartis, Pfizer, and BMS; Dr Hong Hua is an employee of Prometheus Laboratories Inc; Dr. Howard L. Kaufman reports honoraria from Alkermes, Amgen, EMD Serono, Merck, Prometheus, and Sanofi; Speakers’ Bureau support from Merck; and has performed in a consulting or advisory role for Prometheus, Alkermes, Amgen, EMD Serono, Merck, and Sanofi; Dr Janice P. Dutcher has performed in a consulting or advisory role for Prometheus, BMS, Tracon, Amgen (Data Safety and Monitoring Committees), Novartis (education); and has received Speakers’ Bureau support from Prometheus and Novartis; Dr Jonathan S. Treisman has performed in an advisory role for Prometheus Laboratories Inc; has received Speakers’ Bureau support from Prometheus Laboratories Inc; and has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Prometheus (speaking, advisory); Dr Joseph I. Clark is an advisory board member for Prometheus and Bayer-Onyx; has received Speakers’ Bureau support from Prometheus, BMS, and Merck; and has received honoraria from Prometheus, BMS, Pfizer, and Merck; Dr Mayer Fishman participated in RCC-related advisory boards for Aveo, Bayer, Eisai, GSK (now part of Novartis), Novartis, Pfizer, and Prometheus; and has received research funding for RCC-related trials from Acceleron, Altor, Aveo, Bayer, Eisai, Exelixis, GSK (now part of Novartis), Merck, Pfizer, Prometheus, and Tracon; Dr Michael A. Morse is an advisory board member for Genentech, Prometheus, Celgene, Ipsen, Novartis, and Lexxicon; has received Speakers’ Bureau support from Genentech, Prometheus, Celgene, and Novartis; has received honoraria from Genentech, Prometheus, Celgene, Ipsen, Novartis, Astellas Bayer, Onyx, and Lexxicon; and has received research funding from BMS, Aduro, Alphavax, and Eisai; Dr Neeraj Agarwal has performed in a consulting or advisory role for Pfizer, Argos, and Exelixis; Dr Peter Van Veldhuizen has acted in a consulting or advisory role for Prometheus and has received Speakers’ Bureau support from Prometheus; Dr Ralph J. Hauke has received honoraria from Best Doctors for second opinion consultations; Dr Rene Gonzalez is an advisory board member for Bayer-Onyx, BMS, Genentech, GSK, Prometheus, and Roche; and has received research funding from Bayer, BMS, Eisai, Genentech, GSK, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, and Roche; Dr Sandra Aung is an employee of Prometheus Laboratories Inc; Dr Sigrun Hallmeyer has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from BMS as part of Speakers’ Bureau; has served in a consulting or advisory role for BMS, Cardinal Health, iCAN, and TPI; has received Speakers’ Bureau support from BMS; and is a member of the Board of Directors for Oncology Specialists SC; Dr Tharak Rao is an employee of Prometheus Laboratories Inc; Dr Ulka Vaishampayan received honoraria and research funding from Prometheus Laboratories Inc; Jessica Perritt is an employee of Prometheus Laboratories Inc. Dr Venkatesh Rudrapatna has stated that he has no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 2014; 64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Molina AM, Motzer RJ. Current algorithms and prognostic factors in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2008; 6(Suppl 1): S7–13. - PubMed
-
- Drucker BJ. Renal cell carcinoma: current status and future prospects. Cancer Treat Rev 2005; 31:536–45. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al. Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: final efficacy and safety results of the phase III treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27:3312–8. - PubMed
-
- Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011; 378:1931–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

