Metformin Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via PKM2 Relative-mTOR/p70s6k Signaling Pathway in Cervical Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 27916907
- PMCID: PMC5187800
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17122000
Metformin Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via PKM2 Relative-mTOR/p70s6k Signaling Pathway in Cervical Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
Background: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays a prominent role in tumorigenesis. Metformin exerts antitumorigenic effects in various cancers. This study investigated the mechanisms of metformin in TGF-β1-induced Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cervical carcinoma cells.
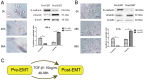
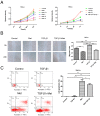
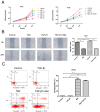
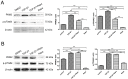
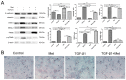
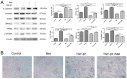
Methods: cells were cultured with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 to induce EMT and treated with or without metformin. Cell viability was evaluated by CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit 8, CCK-8) assay; apoptosis were analyzed by flow cytometry; cell migration was evaluated by wound-healing assay. Western blotting was performed to detect E-cadherin, vimentin, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), snail family transcriptional repressor 2 (SNAIL2), phosphorylation of p70s6k (p-p70s6k) and -Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) Results: TGF-β1 promoted proliferation and migration, and it attenuated apoptosis compared with cells treated with metformin with or without TGF-β1 in cervical carcinoma cells. Moreover, metformin partially abolished TGF-β1-induced EMT cell proliferation and reversed TGF-β1-induced EMT. In addition, the anti-EMT effects of metformin could be partially in accord with rapamycin, a specific mTOR inhibitor. Metformin decreased the p-p70s6k expression and the blockade of mTOR/p70s6k signaling decreased PKM2 expression.
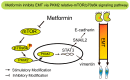
Conclusion: Metformin abolishes TGF-β1-induced EMT in cervical carcinoma cells by inhibiting mTOR/p70s6k signaling to down-regulate PKM2 expression. Our study provides a novel mechanistic insight into the anti-tumor effects of metformin.
Keywords: PKM2; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; mammalian target of rapamycin; metformin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
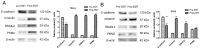
Similar articles
-
Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Decreased Pyruvate Kinase M2 (PKM2) Expression in Cervical Cancer Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Apr 27;23:2017-2028. doi: 10.12659/msm.901542. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28446743 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin Inhibits Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Keloid Fibroblasts via the HIF-1α/PKM2 Signaling Pathway.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jun 10;16(7):960-966. doi: 10.7150/ijms.32157. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31341409 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT through the inhibition of the mTOR pathway by reducing the expression of PKM2 and is closely linked to oxidative stress.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Oct;38(4):1235-42. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2721. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27573422
-
ROS-Nrf2 pathway mediates the development of TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the activation of Notch signaling.Eur J Cell Biol. 2021 Sep-Nov;100(7-8):151181. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2021.151181. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Eur J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34763128 Review.
-
The Impact of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metformin on Pancreatic Cancer Chemoresistance: A Pathway towards Individualized Therapy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Mar 23;58(4):467. doi: 10.3390/medicina58040467. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35454306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesized Honokiol Transfersomes Relieve the Immunosuppressive and Stem-Like Cell Characteristics of the Aggressive B16F10 Melanoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Aug 24;16:5693-5712. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S314472. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34465990 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor pyruvate kinase M2 modulators: a comprehensive account of activators and inhibitors as anticancer agents.RSC Med Chem. 2021 May 17;12(7):1121-1141. doi: 10.1039/d1md00045d. eCollection 2021 Jul 21. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34355179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1 up-regulation on CD4+ T cells promotes pulmonary fibrosis through STAT3-mediated IL-17A and TGF-β1 production.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Sep 26;10(460):eaar8356. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aar8356. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30257954 Free PMC article.
-
Infection by High-Risk Human Papillomaviruses, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Squamous Pre-Malignant or Malignant Lesions of the Uterine Cervix: A Series of Chained Events?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13543. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413543. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caffeic Acid Expands Anti-Tumor Effect of Metformin in Human Metastatic Cervical Carcinoma HTB-34 Cells: Implications of AMPK Activation and Impairment of Fatty Acids De Novo Biosynthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 21;18(2):462. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020462. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28230778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomson S., Buck E., Petti F., Griffin G., Brown E., Ramnarine N., Iwata K.K., Gibson N., Haley J.D. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of sensitivity of non-small-cell lung carcinoma cell lines and xenografts to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9455–9462. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1058. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kurrey N.K., Jalgaonkar S.P., Joglekar A.V., Ghanate A.D., Chaskar P.D., Doiphode R.Y., Bapat S.A. Snail and slug mediate radioresistance and chemoresistance by antagonizing P53-mediated apoptosis and acquiring a stem-like phenotype in ovarian cancer cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27:2059–2068. doi: 10.1002/stem.154. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

