Iron overload across the spectrum of non-transfusion-dependent thalassaemias: role of erythropoiesis, splenectomy and transfusions
- PMID: 27917462
- PMCID: PMC5248634
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.14373
Iron overload across the spectrum of non-transfusion-dependent thalassaemias: role of erythropoiesis, splenectomy and transfusions
Abstract
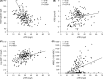
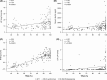
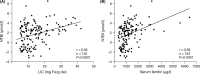
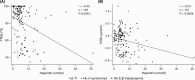
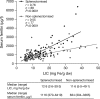
Non-transfusion-dependent thalassaemias (NTDT) encompass a spectrum of anaemias rarely requiring blood transfusions. Increased iron absorption, driven by hepcidin suppression secondary to erythron expansion, initially causes intrahepatic iron overload. We examined iron metabolism biomarkers in 166 NTDT patients with β thalassaemia intermedia (n = 95), haemoglobin (Hb) E/β thalassaemia (n = 49) and Hb H syndromes (n = 22). Liver iron concentration (LIC), serum ferritin (SF), transferrin saturation (TfSat) and non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) were elevated and correlated across diagnostic subgroups. NTBI correlated with soluble transferrin receptor (sTfR), labile plasma iron (LPI) and nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs), with elevations generally confined to previously transfused patients. Splenectomised patients had higher NTBI, TfSat, NRBCs and SF relative to LIC, than non-splenectomised patients. LPI elevations were confined to patients with saturated transferrin. Erythron expansion biomarkers (sTfR, growth differentiation factor-15, NRBCs) correlated with each other and with iron overload biomarkers, particularly in Hb H patients. Plasma hepcidin was similar across subgroups, increased with >20 prior transfusions, and correlated inversely with TfSat, NTBI, LPI and NRBCs. Hepcidin/SF ratios were low, consistent with hepcidin suppression relative to iron overload. Increased NTBI and, by implication, risk of extra-hepatic iron distribution are more likely in previously transfused, splenectomised and iron-overloaded NTDT patients with TfSat >70%.
Keywords: anaemia; ineffective erythropoiesis; iron overload; non-transfusion-dependent thalassaemia.
© 2016 The Authors. British Journal of Haematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Imbalance of erythropoiesis and iron metabolism in patients with thalassemia.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jan 1;16(2):302-310. doi: 10.7150/ijms.27829. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30745811 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary hypertension in non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia: Correlation with clinical parameters, liver iron concentration, and non-transferrin-bound iron.Hematology. 2015 Dec;20(10):610-7. doi: 10.1179/1607845415Y.0000000014. Epub 2015 May 12. Hematology. 2015. PMID: 25964094
-
Mechanisms of plasma non-transferrin bound iron generation: insights from comparing transfused diamond blackfan anaemia with sickle cell and thalassaemia patients.Br J Haematol. 2014 Dec;167(5):692-6. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13081. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Br J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 25209728 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interaction of Transfusion and Iron Chelation in Thalassemias.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2018 Apr;32(2):247-259. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2017.11.010. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2018. PMID: 29458730 Review.
-
Iron overload in thalassemia: different organs at different rates.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2017 Dec 8;2017(1):265-271. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2017.1.265. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2017. PMID: 29222265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thalassemias: An Overview.Int J Neonatal Screen. 2019 Mar 20;5(1):16. doi: 10.3390/ijns5010016. eCollection 2019 Mar. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2019. PMID: 33072976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of oral iron chelators in the management of transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia major based on serum ferritin and liver enzymes.F1000Res. 2023 Dec 19;12:154. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.128810.2. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 39233713 Free PMC article.
-
Gdf15 regulates murine stress erythroid progenitor proliferation and the development of the stress erythropoiesis niche.Blood Adv. 2019 Jul 23;3(14):2205-2217. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000375. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31324641 Free PMC article.
-
Residual erythropoiesis protects against myocardial hemosiderosis in transfusion-dependent thalassemia by lowering labile plasma iron via transient generation of apotransferrin.Haematologica. 2017 Oct;102(10):1640-1649. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.170605. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 28642302 Free PMC article.
-
The Correlation Between Ineffective Erythropoiesis Biomarkers and Development of Extramedullary Hematopoiesis in Patients with Thalassemia.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 1;14(1):e2022052. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2022.052. eCollection 2022. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35865404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bansal, S.S. , Halket, J.M. , Fusova, J. , Bomford, A. , Simpson, R.J. , Vasavda, N. , Thein, S.L. & Hider, R.C. (2009) Quantification of hepcidin using matrix‐assisted laser desorption/ionization time‐of‐flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 23, 1531–1542. - PubMed
-
- Cabantchik, Z.I. , Breuer, W. , Zanninelli, G. & Cianciulli, P. (2005) LPI‐labile plasma iron in iron overload. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology, 18, 277–287. - PubMed
-
- Dussiot, M. , Maciel, T.T. , Fricot, A. , Chartier, C. , Negre, O. , Veiga, J. , Grapton, D. , Paubelle, E. , Payen, E. , Beuzard, Y. , Leboulch, P. , Ribeil, J.A. , Arlet, J.B. , Cote, F. , Courtois, G. , Ginzburg, Y.Z. , Daniel, T.O. , Chopra, R. , Sung, V. , Hermine, O. & Moura, I.C. (2014) An activin receptor IIA ligand trap corrects ineffective erythropoiesis in beta‐thalassemia. Nature Medicine, 20, 398–407. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Esposito, B.P. , Breuer, W. , Sirankapracha, P. , Pootrakul, P. , Hershko, C. & Cabantchik, Z.I. (2003) Labile plasma iron in iron overload: redox activity and susceptibility to chelation. Blood, 102, 2670–2677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

