Α Markov model for longitudinal studies with incomplete dichotomous outcomes
- PMID: 27917593
- PMCID: PMC5363348
- DOI: 10.1002/pst.1794
Α Markov model for longitudinal studies with incomplete dichotomous outcomes
Abstract
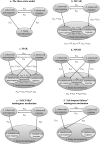
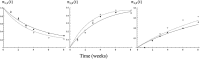
Missing outcome data constitute a serious threat to the validity and precision of inferences from randomized controlled trials. In this paper, we propose the use of a multistate Markov model for the analysis of incomplete individual patient data for a dichotomous outcome reported over a period of time. The model accounts for patients dropping out of the study and also for patients relapsing. The time of each observation is accounted for, and the model allows the estimation of time-dependent relative treatment effects. We apply our methods to data from a study comparing the effectiveness of 2 pharmacological treatments for schizophrenia. The model jointly estimates the relative efficacy and the dropout rate and also allows for a wide range of clinically interesting inferences to be made. Assumptions about the missingness mechanism and the unobserved outcomes of patients dropping out can be incorporated into the analysis. The presented method constitutes a viable candidate for analyzing longitudinal, incomplete binary data.
Keywords: Bayesian analysis; missing data; multistate models.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors Pharmaceutical Statistics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Wahlbeck K., Tuunainen A., Ahokas A., Leucht S., Psychopharmacology 2001, 155, 230. - PubMed
-
- Little R., Rubin D., Statistical analysis with missing data, 2nd ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York: 2002.
-
- White I. R., Thompson S. G., Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 993. - PubMed
-
- Donders A. R. T., van der Heijden G. J. M. G., Stijnen T., Moons K. G. M., J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2006, 59, 1087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

