Epidemiology of occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis; reports from the SWORD scheme in the UK from 1996 to 2015
- PMID: 27919062
- PMCID: PMC5520266
- DOI: 10.1136/oemed-2016-103838
Epidemiology of occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis; reports from the SWORD scheme in the UK from 1996 to 2015
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the reported incidence of occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis (OHP) in the UK and to consider whether the pattern of attributed causation has changed over time.
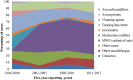
Methods: All cases of OHP reported to the SWORD scheme between January 1996 and December 2015 were classified into 1 of 10 categories of the suspected agent. Cases were grouped into four 5-year time periods to examine any changing pattern in incidence or suspected causation. For each time period, the annual incidence was calculated using the estimated number of reported cases and the working population of the UK.
Results: Between 1996 and 2015, there were 202 actual cases of OHP reported to SWORD, equating to an estimated 818 cases, when adjusting for the sampling ratio. Over this period, the annual UK incidence was 1.4 per million workers. The mean (SD) age of reported cases was 52 (13) years, and cases were four-times more likely to be men than women. Over the study period, there was a fall in the proportion of cases reported to be due to agricultural exposures (44-12%), and an increase in cases due to metalworking fluids (MWFs, 2-45%).
Conclusions: Over the last 20 years, the incidence of OHP in the UK has been ∼1-2 cases per million workers per year. Working with water-based MWFs is now the most commonly suspected causative exposure for OHP cases reported to the SWORD scheme in the UK.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Demedts M, Wells AU, Anto JM, et al. Interstitial lung diseases: an epidemiological overview. Eur Respir J Suppl 2001;32:2s–16s. - PubMed
-
- Office for National Statistics Time Series: Employment release date, 16 March 2016. http://www.ons.gov.uk/employmentandlabourmarket/peopleinwork/employmenta....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical