Three-dimensional Modelling of the Voltage-gated Sodium Ion Channel from Anopheles gambiae Reveals Spatial Clustering of Evolutionarily Conserved Acidic Residues at the Extracellular Sites
- PMID: 27919210
- PMCID: PMC5725538
- DOI: 10.2174/1567201814666161205131213
Three-dimensional Modelling of the Voltage-gated Sodium Ion Channel from Anopheles gambiae Reveals Spatial Clustering of Evolutionarily Conserved Acidic Residues at the Extracellular Sites
Abstract
Background: The eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel(e-Nav) is a large asymmetric transmembrane protein with important functions concerning neurological function. No structure has been resolved at high resolution for this protein.
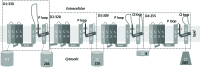
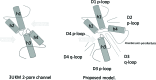
Methods: A homology model of the transmembrane and extracellular regions of an Anopheles gambiae para-like channel with emphasis on the pore entrance has been constructed, based upon the templates provided by a prokaryotic sodium channel and a potassium two-pore channel. The latter provides a template for the extracellular regions, which are located above the entrance to the pore, which is likely to open at a side of a dome formed by these loops.
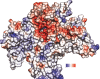
Results: A model created with this arrangement shows a structure similar to low-resolution cryoelectron microscope images of a related structure. The pore entrance also shows favorable electrostatic interface.
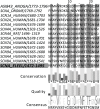
Conclusion: Residues responsible for the negative charge around the pore have been traced in phylogeny to highlight their importance. This model is intended for the study of pore-blocking toxins.
Keywords: Eukaryotic voltage gated sodium channel; anopheles.; extracellular interface; homology model; pore blocker; toxin; transmembrane.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures




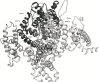
References
-
- Hodgkin A.L., Huxley A.F., Katz B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. 1952;116(4):424–448. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1113/ jphysiol.1952.sp004716]. [PMID: 14946712]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hodgkin A.L., Huxley A.F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. 1952;116(4):449–472. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1113/ jphysiol.1952.sp004717]. [PMID: 14946713]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hodgkin A.L., Huxley A.F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. 1952;116(4):497–506. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol. 1952.sp004719]. [PMID: 14946715]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duclohier H. Structure-function studies on the voltage-gated sodium channel. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1788(11):2374–2379. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.08.017]. [PMID: 19747894]. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
