Advax, a Delta Inulin Microparticle, Potentiates In-built Adjuvant Property of Co-administered Vaccines
- PMID: 27919753
- PMCID: PMC5233800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.11.015
Advax, a Delta Inulin Microparticle, Potentiates In-built Adjuvant Property of Co-administered Vaccines
Abstract
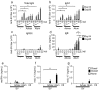
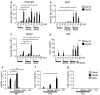
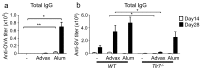
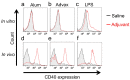
Advax, a delta inulin-derived microparticle, has been developed as an adjuvant for several vaccines. However, its immunological characteristics and potential mechanism of action are yet to be elucidated. Here, we show that Advax behaves as a type-2 adjuvant when combined with influenza split vaccine, a T helper (Th)2-type antigen, but behaves as a type-1 adjuvant when combined with influenza inactivated whole virion (WV), a Th1-type antigen. In addition, an adjuvant effect was not observed when Advax-adjuvanted WV vaccine was used to immunize toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 knockout mice which are unable to respond to RNA contained in WV antigen. Similarly, no adjuvant effect was seen when Advax was combined with endotoxin-free ovalbumin, a neutral Th0-type antigen. An adjuvant effect was also not seen in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α knockout mice, and the adjuvant effect required the presences of dendritic cells (DCs) and phagocytic macrophages. Therefore, unlike other adjuvants, Advax potentiates the intrinsic or in-built adjuvant property of co-administered antigens. Hence, Advax is a unique class of adjuvant which can potentiate the intrinsic adjuvant feature of the vaccine antigens through a yet to be determined mechanism.
Keywords: Adjuvant; Inulin; Macrophage; Particle; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aoshi T., Zinselmeyer B.H., Konjufca V., Lynch J.N., Zhang X., Koide Y., Miller M.J. Bacterial entry to the splenic white pulp initiates antigen presentation to CD8 + T cells. Immunity. 2008;29:476–486. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

