N-Acetyl-l-Cysteine and Cysteamine as New Strategies against Mixed Biofilms of Nonencapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae and Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae
- PMID: 27919900
- PMCID: PMC5278723
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01992-16
N-Acetyl-l-Cysteine and Cysteamine as New Strategies against Mixed Biofilms of Nonencapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae and Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae
Abstract
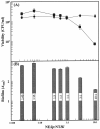
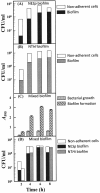
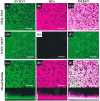
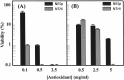
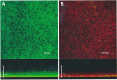
Acute otitis media, a polymicrobial disease of the middle ear cavity of children, is a significant public health problem worldwide. It is most frequently caused by encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae and nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae, although the widespread use of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines is apparently producing an increase in the carriage of nonencapsulated S. pneumoniae Frequently, pneumococci and H. influenzae live together in the human nasopharynx, forming a self-produced biofilm. Biofilms present a global medical challenge since the inherent antibiotic resistance of their producers demands the use of large doses of antibiotics over prolonged periods. Frequently, these therapeutic measures fail, contributing to bacterial persistence. Here, we describe the development of an in vitro nonencapsulated S. pneumoniae-nontypeable H. influenzae biofilm system with polystyrene or glass-bottom plates. Confocal laser scanning microscopy and specific fluorescent labeling of pneumococcal cells with Helix pomatia agglutinin revealed an even distribution of both species within the biofilm. This simple and robust protocol of mixed biofilms was used to test the antimicrobial properties of two well-known antioxidants that are widely used in the clinical setting, i.e., N-acetyl-l-cysteine and cysteamine. This repurposing approach showed the high potency of N-acetyl-l-cysteine and cysteamine against mixed biofilms of nonencapsulated S. pneumoniae and nontypeable H. influenzae Decades of clinical use mean that these compounds are safe to use, which may accelerate their evaluation in humans.
Keywords: Haemophilus influenzae; Streptococcus pneumoniae; antioxidants; biofilms.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonencapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae causes otitis media during single-species infection and during polymicrobial infection with nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae.Pathog Dis. 2015 Jul;73(5):ftu011. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftu011. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26014114 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm production by Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from the nasopharynx of children with acute otitis media.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jan 11;19(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3657-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30634919 Free PMC article.
-
Widening the antimicrobial spectrum of esters of bicyclic amines: In vitro effect on gram-positive Streptococcus pneumoniae and gram-negative non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae biofilms.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019 Jan;1863(1):96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019. PMID: 30292448
-
Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae: living together in a biofilm.Pathog Dis. 2013 Nov;69(2):114-26. doi: 10.1111/2049-632X.12073. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Pathog Dis. 2013. PMID: 23913525 Review.
-
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a pathogen in children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009 Jan;28(1):43-8. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318184dba2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009. PMID: 19057458 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Antibiofilm Effect of N-Acetyl-L-cysteine/Dry Propolis Extract Combination on Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Upper Respiratory Tract Infections.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;16(11):1604. doi: 10.3390/ph16111604. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004469 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of N-acetylcysteine against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Burkholderia cepacia complex grown in planktonic phase and biofilm.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 1;13(10):e0203941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203941. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30273348 Free PMC article.
-
N-Acetylcysteine as Adjuvant Therapy for COVID-19 - A Perspective on the Current State of the Evidence.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Jul 6;14:2993-3013. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S306849. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34262324 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence Imaging of Streptococcus pneumoniae with the Helix pomatia agglutinin (HPA) As a Potential, Rapid Diagnostic Tool.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 18;8:1333. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01333. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28769901 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Lethal Effects of N-Acetylcysteine on Xylella fastidiosa Strain De Donno Biofilm Formation and Detachment.Microorganisms. 2019 Dec 5;7(12):656. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120656. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31817370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klein JO. 2000. The burden of otitis media. Vaccine 19(Suppl 1):S2–S8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

