The molecular pathogenesis of schwannomatosis, a paradigm for the co-involvement of multiple tumour suppressor genes in tumorigenesis
- PMID: 27921248
- PMCID: PMC5258795
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-016-1753-8
The molecular pathogenesis of schwannomatosis, a paradigm for the co-involvement of multiple tumour suppressor genes in tumorigenesis
Abstract
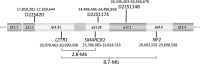
Schwannomatosis is characterized by the predisposition to develop multiple schwannomas and, less commonly, meningiomas. Despite the clinical overlap with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), schwannomatosis is not caused by germline NF2 gene mutations. Instead, germline mutations of either the SMARCB1 or LZTR1 tumour suppressor genes have been identified in 86% of familial and 40% of sporadic schwannomatosis patients. In contrast to patients with rhabdoid tumours, which are due to complete loss-of-function SMARCB1 mutations, individuals with schwannomatosis harbour predominantly hypomorphic SMARCB1 mutations which give rise to the synthesis of mutant proteins with residual function that do not cause rhabdoid tumours. Although biallelic mutations of SMARCB1 or LZTR1 have been detected in the tumours of patients with schwannomatosis, the classical two-hit model of tumorigenesis is insufficient to account for schwannoma growth, since NF2 is also frequently inactivated in these tumours. Consequently, tumorigenesis in schwannomatosis must involve the mutation of at least two different tumour suppressor genes, an occurrence frequently mediated by loss of heterozygosity of large parts of chromosome 22q harbouring not only SMARCB1 and LZTR1 but also NF2. Thus, schwannomatosis is paradigmatic for a tumour predisposition syndrome caused by the concomitant mutational inactivation of two or more tumour suppressor genes. This review provides an overview of current models of tumorigenesis and mutational patterns underlying schwannomatosis that will ultimately help to explain the complex clinical presentation of this rare disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are unaware of any conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Agnihotri S, Jalali S, Wilson MR, Danesh A, Li M, Klironomos G, Krieger JR, Mansouri A, Khan O, Mamatjan Y, Landon-Brace N, Tung T, Dowar M, Li T, Bruce JP, Burrell KE, Tonge PD, Alamsahebpour A, Krischek B, Agarwalla PK, Bi WL, Dunn IF, Beroukhim R, Fehlings MG, Bril V, Pagnotta SM, Iavarone A, Pugh TJ, Aldape KD, Zadeh G. The genomic landscape of schwannoma. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1339–1348. doi: 10.1038/ng.3688. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ambrogio C, Gómez-López G, Falcone M, Vidal A, Nadal E, Crosetto N, Blasco RB, Fernández-Marcos PJ, Sánchez-Céspedes M, Ren X, Wang Z, Ding K, Hidalgo M, Serrano M, Villanueva A, Santamaría D, Barbacid M. Combined inhibition of DDR1 and Notch signaling is a therapeutic strategy for KRAS-driven lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Med. 2016;22:270–277. doi: 10.1038/nm.4041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ammerlaan AC, Ararou A, Houben MP, Baas F, Tijssen CC, Teepen JL, Wesseling P, Hulsebos TJ. Long-term survival and transmission of INI1-mutation via nonpenetrant males in a family with rhabdoid tumour predisposition syndrome. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:474–479. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604156. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

