Convex Analysis of Mixtures for Separating Non-negative Well-grounded Sources
- PMID: 27922124
- PMCID: PMC5138607
- DOI: 10.1038/srep38350
Convex Analysis of Mixtures for Separating Non-negative Well-grounded Sources
Abstract
Blind Source Separation (BSS) is a powerful tool for analyzing composite data patterns in many areas, such as computational biology. We introduce a novel BSS method, Convex Analysis of Mixtures (CAM), for separating non-negative well-grounded sources, which learns the mixing matrix by identifying the lateral edges of the convex data scatter plot. We propose and prove a sufficient and necessary condition for identifying the mixing matrix through edge detection in the noise-free case, which enables CAM to identify the mixing matrix not only in the exact-determined and over-determined scenarios, but also in the under-determined scenario. We show the optimality of the edge detection strategy, even for cases where source well-groundedness is not strictly satisfied. The CAM algorithm integrates plug-in noise filtering using sector-based clustering, an efficient geometric convex analysis scheme, and stability-based model order selection. The superior performance of CAM against a panel of benchmark BSS techniques is demonstrated on numerically mixed gene expression data of ovarian cancer subtypes. We apply CAM to dissect dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging data taken from breast tumors and time-course microarray gene expression data derived from in-vivo muscle regeneration in mice, both producing biologically plausible decomposition results.
Figures
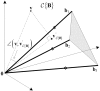
 denotes the angle between two input vectors.
denotes the angle between two input vectors.



References
-
- Lee D. D. & Seung H. S. Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 401, 788–791 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Chan T.-H., Ma W.-K., Chi C.-Y. & Wang Y. A convex analysis framework for blind separation of non-negative sources. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 56, 5120–5134 (2008).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

