Expression of microRNA-328 Functions as a Biomarker for Recurrence of Early Gastric Cancer (EGC) After Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) by Modulating CD44
- PMID: 27923017
- PMCID: PMC5147686
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.896225
Expression of microRNA-328 Functions as a Biomarker for Recurrence of Early Gastric Cancer (EGC) After Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) by Modulating CD44
Abstract
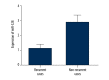
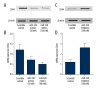
BACKGROUND This study investigated the molecular mechanism of the effect of CD44 on the recurrence of EGC after ESD, including the potential regulator and signaling pathways of CD44. MATERIAL AND METHODS We searched the miRNA online database (www.mirdb.org) with the "seed sequence" located within the 3'-UTR of the target gene, and performed luciferase assay to test the miRNA/mRNA relationship. We also determined the expression of CD44 in the EGC and control samples. In addition, statistical analysis was used to explore the role of miR-328 as a biomarker to predict the recurrence after ECD. RESULTS We validated CD44 to be the direct gene via luciferase reporter assay system. We also established the negative regulatory relationship between miR-328 and CD44 via studying the relative luciferase activity at different concentrations of miR-328 mimics. We also conducted real-time PCR and Western blot analysis to study the mRNA and protein expression level of CD44 among different groups (recurrence-positive and recurrence-negative) or cells treated with different concentrations of miR-328 mimics/inhibitors, indicating the negative regulatory relationship between miR-328 and CD44. We also investigated the relative viability of EGC cells when transfected with miR-328 mimics (50 nM and 100 nM) and miR-328 inhibitors (100 nM) to validate miR-328 to be negatively interfering with the viability of EGC cells. miR-328 was also recognized as a potential biomarker to predict recurrence after ESD in EGC patients via analysis of the recurrence-free rate among different groups of EGC patients. CONCLUSIONS The expression level of miR-328 can function as a predictive biomarker of recurrence after ECD in patients with EGC via targeting CD44.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- Correa P. International cancer epidemiology meetings. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1992;1(3):245–57. - PubMed
-
- Gotoda T, Yamamoto H, Soetikno RM. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41(10):929–42. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka M, Ono H, Hasuike N, Takizawa K. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. Digestion. 2008;77(Suppl 1):23–28. - PubMed
-
- Nagano H, Ohyama S, Fukunaga T, et al. Indications for gastrectomy after incomplete EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2005;8(3):149–54. - PubMed
-
- Toyokawa T, Inaba T, Omote S, et al. Risk factors for perforation and delayed bleeding associated with endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: analysis of 1123 lesions. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(5):907–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

