Widespread control of calcium signaling by a family of SERCA-inhibiting micropeptides
- PMID: 27923914
- PMCID: PMC5696797
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aaj1460
Widespread control of calcium signaling by a family of SERCA-inhibiting micropeptides
Abstract
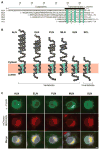
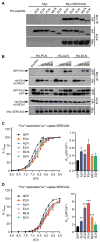
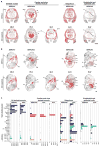
Micropeptides function as master regulators of calcium-dependent signaling in muscle. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA), the membrane pump that promotes muscle relaxation by taking up Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, is directly inhibited by three muscle-specific micropeptides: myoregulin (MLN), phospholamban (PLN), and sarcolipin (SLN). The widespread and essential function of SERCA across diverse cell types has raised questions as to how SERCA is regulated in cells that lack MLN, PLN, and SLN. We identified two transmembrane micropeptides, endoregulin (ELN) and another-regulin (ALN), that share key amino acids with their muscle-specific counterparts and function as direct inhibitors of SERCA pump activity. The distribution of transcripts encoding ELN and ALN mirrored that of SERCA isoform-encoding transcripts in nonmuscle cell types. Our findings identify additional members of the SERCA-inhibitory micropeptide family, revealing a conserved mechanism for the control of intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in both muscle and nonmuscle cell types.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
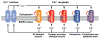
References
-
- Rizzuto R, Pozzan T. Microdomains of intracellular Ca2+: Molecular determinants and functional consequences. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:369–408. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Unlocking the secrets of cell signaling. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE. Calcium signaling. Cell. 2007;131:1047–1058. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–529. - PubMed
-
- Rossi AE, Dirksen RT. Sarcoplasmic reticulum: The dynamic calcium governor of muscle. Muscle Nerve. 2006;33:715–731. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

