AraPheno: a public database for Arabidopsis thaliana phenotypes
- PMID: 27924043
- PMCID: PMC5210660
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw986
AraPheno: a public database for Arabidopsis thaliana phenotypes
Abstract
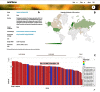
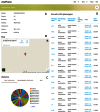
Natural genetic variation makes it possible to discover evolutionary changes that have been maintained in a population because they are advantageous. To understand genotype-phenotype relationships and to investigate trait architecture, the existence of both high-resolution genotypic and phenotypic data is necessary. Arabidopsis thaliana is a prime model for these purposes. This herb naturally occurs across much of the Eurasian continent and North America. Thus, it is exposed to a wide range of environmental factors and has been subject to natural selection under distinct conditions. Full genome sequencing data for more than 1000 different natural inbred lines are available, and this has encouraged the distributed generation of many types of phenotypic data. To leverage these data for meta analyses, AraPheno (https://arapheno.1001genomes.org) provide a central repository of population-scale phenotypes for A. thaliana inbred lines. AraPheno includes various features to easily access, download and visualize the phenotypic data. This will facilitate a comparative analysis of the many different types of phenotypic data, which is the base to further enhance our understanding of the genotype-phenotype map.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

