State of newborn health in India
- PMID: 27924104
- PMCID: PMC5144119
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2016.183
State of newborn health in India
Abstract
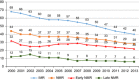
About 0.75 million neonates die every year in India, the highest for any country in the world. The neonatal mortality rate (NMR) declined from 52 per 1000 live births in 1990 to 28 per 1000 live births in 2013, but the rate of decline has been slow and lags behind that of infant and under-five child mortality rates. The slower decline has led to increasing contribution of neonatal mortality to infant and under-five mortality. Among neonatal deaths, the rate of decline in early neonatal mortality rate (ENMR) is much lower than that of late NMR. The high level and slow decline in early NMR are also reflected in a high and stagnant perinatal mortality rate. The rate of decline in NMR, and to an extent ENMR, has accelerated with the introduction of National Rural Health Mission in mid-2005. Almost all states have witnessed this phenomenon, but there is still a huge disparity in NMR between and even within the states. The disparity is further compounded by rural-urban, poor-rich and gender differentials. There is an interplay of different demographic, educational, socioeconomic, biological and care-seeking factors, which are responsible for the differentials and the high burden of neonatal mortality. Addressing inequity in India is an important cross-cutting action that will reduce newborn mortality.
Figures
References
-
- Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, Perin J, Rudan I, Lawn JE et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015; 385(9966): 430–440. - PubMed
-
- Registrar General of India. Sample registration system (SRS) statistical report 2013. New Delhi: 2013.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Data. Available at http://data.un.org/Explorer.aspx?d=WHO (accessed on 20 August 2014).
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, Perin J, Scott S, Lawn JE et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet 2012; 379: 2151–2161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical