EEG functional network topology is associated with disability in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 27924954
- PMCID: PMC5141491
- DOI: 10.1038/srep38653
EEG functional network topology is associated with disability in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
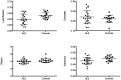
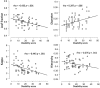
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is one of the most severe neurodegenerative diseases, which is known to affect upper and lower motor neurons. In contrast to the classical tenet that ALS represents the outcome of extensive and progressive impairment of a fixed set of motor connections, recent neuroimaging findings suggest that the disease spreads along vast non-motor connections. Here, we hypothesised that functional network topology is perturbed in ALS, and that this reorganization is associated with disability. We tested this hypothesis in 21 patients affected by ALS at several stages of impairment using resting-state electroencephalography (EEG) and compared the results to 16 age-matched healthy controls. We estimated functional connectivity using the Phase Lag Index (PLI), and characterized the network topology using the minimum spanning tree (MST). We found a significant difference between groups in terms of MST dissimilarity and MST leaf fraction in the beta band. Moreover, some MST parameters (leaf, hierarchy and kappa) significantly correlated with disability. These findings suggest that the topology of resting-state functional networks in ALS is affected by the disease in relation to disability. EEG network analysis may be of help in monitoring and evaluating the clinical status of ALS patients.
Figures

References
-
- Del Aguila M., Longstreth W., McGuire V., Koepsell T. & Van Belle G. Prognosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis a population-based study. Neurology 60, 813–819 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Chiò A. et al.. Neuroimaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: insights into structural and functional changes. The Lancet Neurology 13, 1228–1240 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Stam C. v. & Van Straaten E. The organization of physiological brain networks. Clinical neurophysiology 123, 1067–1087 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Stam C. J. Modern network science of neurological disorders. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 15, 683–695 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

