The prediction of radiofrequency ablation zone volume using vascular indices of 3-dimensional volumetric colour Doppler ultrasound in an in vitro blood-perfused bovine liver model
- PMID: 27925468
- PMCID: PMC5685127
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20160661
The prediction of radiofrequency ablation zone volume using vascular indices of 3-dimensional volumetric colour Doppler ultrasound in an in vitro blood-perfused bovine liver model
Abstract
Objective: To determine the most reliable predictor of radiofrequency (RF) ablation zone volume among three-dimensional (3D) volumetric colour Doppler vascular indices in an in vitro blood-perfused bovine liver model.
Methods: 3D colour Doppler volume data of the local hepatic parenchyma were acquired from 37 areas of 13 bovine livers connected to an in vitro oxygenated blood perfusion system. Doppler vascular indices of vascularization index (VI), flow index (FI) and vascularization flow index (VFI) were obtained from the volume data using 3D volume analysis software. 37 RF ablations were performed at the same locations where the ultrasound data were obtained from. The relationship of these vascular indices and the ablation zone volumes measured from gross specimens were analyzed using a general linear mixed model fit with random effect for liver and backward stepwise regression analysis.
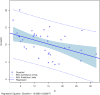
Results: FI was significantly associated with ablation zone volumes measured on gross specimens (p = 0.0047), but explained little of the variance (Rβ2 = 0.21). Ablation zone volume decreased by 0.23 cm3 (95% confidence interval: -0.38, -0.08) for every 1 increase in FI. Neither VI nor VFI was significantly associated with ablation zone volumes (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Although FI was associated with ablation zone volumes, it could not sufficiently explain their variability, limiting its clinical applicability. VI, FI and VFI are not clinically useful in the prediction of RF ablation zone volume in the liver. Advances in knowledge: Despite a significant association of FI with ablation zone volumes, VI, FI and VFI cannot be used for their prediction. Different Doppler vascular indices need to be investigated for clinical use.
Figures

References
-
- Montgomery RS, Rahal A, Dodd GD, 3rd, Leyendecker JR, Hubbard LG. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: variability of lesion size using a single ablation device. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004; 182: 657–61. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.182.3.1820657 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Dodd GD, 3rd, Lanctot AC. Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: effect of variation of portal venous blood flow on lesion size in an in-vitro perfused bovine liver. Acad Radiol 2012; 19: 1018–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2012.04.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang CH, Yu CH, Ko HC, Chang FM, Chen HY. Assessment of normal fetal liver blood flow using quantitative free-dimensional power Doppler ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 2003; 29: 943–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-5629(03)00909-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Raine-Fenning NJ, Ramnarine KV, Nordin NM, Campbell BK. Quantification of blood perfusion using 3D power Doppler: an in-vitro flow phantom study. J Phys Conf Ser 2004; 1: 181–6.
-
- Dubiel M, Hammid A, Breborowicz A, Pietryga M, Sladkevicius P, Olofsson PA, et al. . Flow index evaluation of 3D volume flow images: an in vivo and in vitro study. Ultrasound Med Biol 2006; 32: 665–71. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2006.01.016 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

