The immunomodulatory effects of TNF-α inhibitors on human Th17 cells via RORγt histone acetylation
- PMID: 27926504
- PMCID: PMC5352343
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13791
The immunomodulatory effects of TNF-α inhibitors on human Th17 cells via RORγt histone acetylation
Abstract
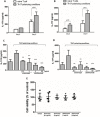
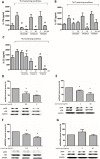
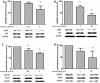
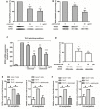
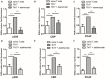
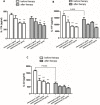
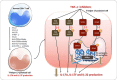
The presence of interleukin (IL)-17-related cytokines correlates with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis. Epigenetic modifications, including histone acetylation, regulate gene expression in RA pathogenesis. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors such as etanercept and adalimumab, represent a breakthrough in RA treatment. We aimed to investigate the effects of etanercept and adalimumab on human Th17-polarized cells and the possible intracellular regulators of these effects, including the Th17-specific transcription factors signal transducer, activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), retinoid-related orphan receptor γ-T (RORγt) and epigenetic modification. Human CD4+ T cells from healthy subjects and patients with RA were pretreated with TNF-α inhibitors and then being polarized into IL-17-producing cells. The Th17-related cytokine levels in the culture supernatants were determined with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Intracellular signalling was investigated by western blot, real-time RT-PCR, and chromatin immunoprecipitation. Th17-polarized cells from patients with RA produced more IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-22 than those from healthy subjects. Etanercept and adalimumab suppressed IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-22 levels in Th17-polarized cells from healthy subjects and patients with RA. Western blot analysis revealed that etanercept and adalimumab decreased mitogen-activated protein kinase-phospho-p38, nuclear factor-κB-phospho-p65, phospho-STAT3 and RORγt levels. Etanercept and adalimumab decreased histone (H)3 and H4 acetylation in the RORγt gene promotor region by decreasing the recruitment of the acetyltransferases p300, CBP and PCAF. The present study broadens our knowledge of the mechanisms underlying the immunomodulatory effects of TNF-α inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis treatment.
Keywords: RORγt; TNF-α; Th17; histone acetylation; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors suppress CCL2 chemokine in monocytes via epigenetic modification.Mol Immunol. 2017 Mar;83:82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.01.009. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28113136
-
AT-rich-interactive domain-containing protein 5A functions as a negative regulator of retinoic acid receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor γt-induced Th17 cell differentiation.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 May;66(5):1185-94. doi: 10.1002/art.38324. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24782182
-
Th17 cells are restrained by Treg cells via the inhibition of interleukin-6 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis responding to anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody therapy.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Oct;64(10):3129-38. doi: 10.1002/art.34565. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22674488
-
Prostaglandin E2 and IL-23 interconnects STAT3 and RoRγ pathways to initiate Th17 CD4+ T-cell development during rheumatoid arthritis.Inflamm Res. 2018 Jul;67(7):589-596. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1153-8. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29713730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations between PTPRC rs10919563 A/G and FCGR2A R131H polymorphisms and responsiveness to TNF blockers in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Jun;36(6):837-44. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3476-5. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 27074847 Review.
Cited by
-
An herbal formula attenuates collagen-induced arthritis via inhibition of JAK2-STAT3 signaling and regulation of Th17 cells in mice.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 4;8(27):44242-44254. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17797. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28562338 Free PMC article.
-
Digoxin mitigates diethylnitrosamine-induced acute liver injury in mice via limiting production of inflammatory mediators.Saudi Pharm J. 2022 Mar;30(3):291-299. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.01.007. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Saudi Pharm J. 2022. PMID: 35498227 Free PMC article.
-
Rejection of intestinal allotransplants is driven by memory T helper type 17 immunity and responds to infliximab.Am J Transplant. 2021 Mar;21(3):1238-1254. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16283. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 32882110 Free PMC article.
-
Nobiletin suppresses the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mediated by modulation of T helper 17 cell differentiation.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2021 Sep;69(2):145-150. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.20-178. Epub 2021 Mar 25. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34616106 Free PMC article.
-
Biologic Drugs for Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Context of Biosimilars, Genetics, Epigenetics and COVID-19 Treatment.Cells. 2021 Feb 4;10(2):323. doi: 10.3390/cells10020323. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33557301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azizi G, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Mirshafiey A. Th17 Cells in Immunopathogenesis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013;16:243–253. - PubMed
-
- Shen H, Goodall JC, Hill Gaston JS. Frequency and phenotype of peripheral blood Th17 cells in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1647–1656. - PubMed
-
- Chabaud M, Durand JM, Buchs N, Fossiez F, Page G, Frappart L, Miossec P. Human interleukin-17: A T cell-derived proinflammatory cytokine produced by the rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Metawi SA, Abbas D, Kamal MM, Ibrahim MK. Serum and synovial fluid levels of interleukin-17 in correlation with disease activity in patients with RA. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30:1201–1207. - PubMed
-
- Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Silman AJ, Symmons DP. Predictors of response to anti-TNF-alpha therapy among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:1558–1565. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

