Multipoint Pacing versus conventional ICD in Patients with a Narrow QRS complex (MPP Narrow QRS trial): study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27927248
- PMCID: PMC5143452
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1698-1
Multipoint Pacing versus conventional ICD in Patients with a Narrow QRS complex (MPP Narrow QRS trial): study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Despite an intensive search for predictors of the response to cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), the QRS duration remains the simplest and most robust predictor of a positive response. QRS duration of ≥ 130 ms is considered to be a prerequisite for CRT; however, some studies have shown that CRT may also be effective in heart failure (HF) patients with a narrow QRS (<130 ms). Since CRT can now be performed by pacing the left ventricle from multiple vectors via a single quadripolar lead, it is possible that multipoint pacing (MPP) might be effective in HF patients with a narrow QRS. This article reports the design of the MPP Narrow QRS trial, a prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled feasibility study to investigate the efficacy of MPP using two LV pacing vectors in patients with a narrow QRS complex (100-130 ms).
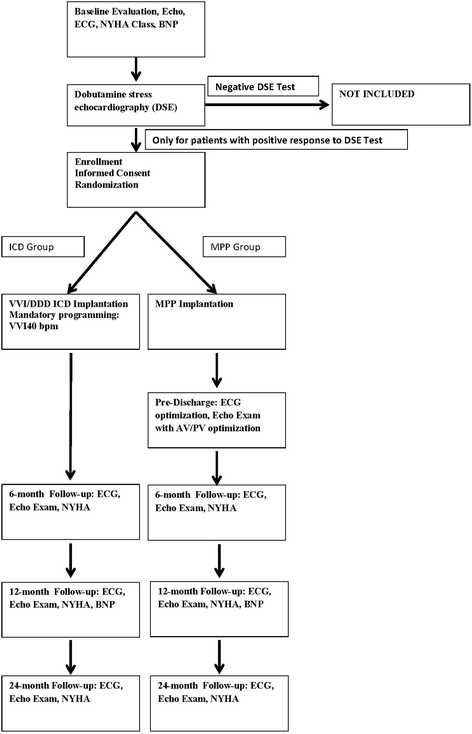
Methods: Fifty patients with a standard ICD indication will be enrolled and randomized (1:1) to either an MPP group or a Standard ICD group. All patients will undergo a low-dose dobutamine stress echo test and only those with contractile reserve will be included in the study and randomized. The primary endpoint will be the percentage of patients in each group that have reverse remodeling at 12 months, defined as a reduction in left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV) of >15% from the baseline.
Discussion: This feasibility study will determine whether MPP improves reverse remodeling, as compared with standard ICD, in HF patients who have a narrow QRS complex (100-130 ms).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02402816 . Registered on 25 March 2015.
Keywords: Cardiac resynchronization therapy; Heart failure; ICD; Multipoint pacing; Narrow QRS.
Figures
References
-
- Bristow MR, Saxon LA, Boehmer J, Krueger S, Kass DA, De Marco T, Carson P, DiCarlo L, DeMets D, White BG, DeVries DW, Feldman AM. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy with or without an implantable defibrillator in advanced chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2140–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032423. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Falk V, González-Juanatey JR, Harjola V-P, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GMC, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. EHJ. 2016;37(27):2129–200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brignole M, Auricchio A, Baron-Esquivias G, Bordachar P, Boriani G, Breithardt OA, Cleland J, Deharo JC, Delgado V, Elliott PM, Gorenek B, Israel CW, Leclercq C, Linde C, Mont L, Padeletti L, Sutton R, Vardas PE, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Fagard R, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Sirnes PA, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Document R, Kirchhof P, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Badano LP, Aliyev F, Bänsch D, Baumgartner H, Bsata W, Buser P, Charron P, Daubert JC, Dobreanu D, Faerestrand S, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Le Heuzey JY, Mavrakis H, McDonagh T, Merino JL, Nawar MM, Nielsen JC, Pieske B, Poposka L, Ruschitzka F, Tendera M, Van Gelder IC, Wilson CM. 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2281–329. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht150. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous