In vitro patterning of pluripotent stem cell-derived intestine recapitulates in vivo human development
- PMID: 27927684
- PMCID: PMC5358103
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.138453
In vitro patterning of pluripotent stem cell-derived intestine recapitulates in vivo human development
Abstract
The intestine plays a central role in digestion, nutrient absorption and metabolism, with individual regions of the intestine having distinct functional roles. Many examples of region-specific gene expression in the adult intestine are known, but how intestinal regional identity is established during development is a largely unresolved issue. Here, we have identified several genes that are expressed in a region-specific manner in the developing human intestine. Using human embryonic stem cell-derived intestinal organoids, we demonstrate that the duration of exposure to active FGF and WNT signaling controls regional identity. Short-term exposure to FGF4 and CHIR99021 (a GSK3β inhibitor that stabilizes β-catenin) resulted in organoids with gene expression patterns similar to developing human duodenum, whereas longer exposure resulted in organoids similar to ileum. When region-specific organoids were transplanted into immunocompromised mice, duodenum-like organoids and ileum-like organoids retained their regional identity, demonstrating that regional identity of organoids is stable after initial patterning occurs. This work provides insights into the mechanisms that control regional specification of the developing human intestine and provides new tools for basic and translational research.
Keywords: Human; Intestine; Organoid; Patterning; Pluripotent stem cells.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
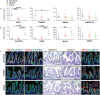
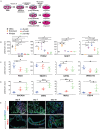
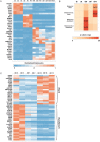
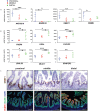

References
-
- Beck C. W. and Slack J. M. (1999). A developmental pathway controlling outgrowth of the Xenopus tail bud. Development 126, 1611-1620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 DK007762/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI116482/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK085532/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007505/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103141/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085532/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD000836/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD012194/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM081879/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103147/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK094775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK091415/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

