Bilateral Tonic Pupils as the Initial Manifestation of Sjögren's Syndrome
- PMID: 27928364
- PMCID: PMC5122921
- DOI: 10.3109/01658107.2015.1067231
Bilateral Tonic Pupils as the Initial Manifestation of Sjögren's Syndrome
Abstract
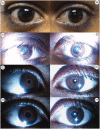
Adie's pupil is characterised by pupil dilatation, segmental iris palsy, light-near dissociation, and slow re-dilatation. Most commonly, tonic pupils are unilateral and idiopathic, but can be caused by orbital disorders and autonomic neuropathies. There are only a few case reports of tonic pupils in patients with Sjögren's syndrome, caused by an autoimmune ciliary ganglionitis. The authors report on two cases with bilateral tonic pupils as the initial manifestation of primary Sjögren's syndrome. Both patients presented with blurred vision, bilateral tonic pupils, and sicca symptoms. The findings suggest that Sjögren's syndrome should be considered in patients presenting with bilateral Adie's tonic pupils.
Keywords: Adie’s tonic pupil; Sjögren’s syndrome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adie's tonic pupil as a manifestation of Sjögren's syndrome.Ital J Neurol Sci. 1997 Oct;18(5):293-5. doi: 10.1007/BF02083307. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1997. PMID: 9412854
-
Adie's syndrome: some new observations.Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1977;75:587-626. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1977. PMID: 613531 Free PMC article.
-
[Tonic pupils in Sjögren's syndrome].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2005 Oct;161(10):963-6. doi: 10.1016/s0035-3787(05)85160-4. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2005. PMID: 16365626 French.
-
[A Case of Anti-GQ1b Antibody Syndrome Associated with Pure Bilateral Adie's Pupils].Brain Nerve. 2016 Jan;68(1):93-6. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416200354. Brain Nerve. 2016. PMID: 26764303 Review. Japanese.
-
Adie's tonic pupil after COVID-19: a case report and literature review.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2024 Apr-Jun;68(2):89-91. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2024.18. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39006340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adie's tonic pupil in primary Sjögren syndrome.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Dec;42(12):3419-3420. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06707-4. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37518192 No abstract available.
-
Adie's Pupil: A Diagnostic Challenge for the Physician.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Mar 8;28:e934657. doi: 10.12659/MSM.934657. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35304432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia as a Presenting Manifestation of Primary Sjögren's Syndrome.Neuroophthalmology. 2016 Sep 7;40(5):247-250. doi: 10.1080/01658107.2016.1218519. eCollection 2016 Oct. Neuroophthalmology. 2016. PMID: 27928415 Free PMC article.
-
Adie's pupil and systemic manifestations: a rare unilateral presentation.GMS Ophthalmol Cases. 2024 Dec 3;14:Doc14. doi: 10.3205/oc000246. eCollection 2024. GMS Ophthalmol Cases. 2024. PMID: 39811490 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglionic Acetylcholine Receptor Antibodies and Autonomic Dysfunction in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 16;21(4):1332. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041332. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32079137 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martinelli P, Minardi C. [Tonic pupil and tendon areflexia: the Holmes-Adie's syndrome]. Recenti Prog Med 2001;92:605–608. [Italian] - PubMed
-
- Lee AG. Tonic Pupil Walham: UpToDate Wolters Kluwer Health; 2014. Available at: http://www.yhdp.net/uptodate/contents/mobipreview.htm?43/5/44117?source=... Updated 23 January 2014. Accessed 15 October 2014
-
- Vetrugno R, Liguori R, Cevoli S, Salvi F, Montagna P. Adie's tonic pupil as a manifestation of Sjögren's syndrome. Ital J Neurol Sci 1997;18:293–295 - PubMed
-
- Newton JL, Frith J, Powell D, Hackett K, Wilton K, Bowman S, Price E, Pease C, Andrews J, Emery P, Hunter J, Gupta M, Vadivelu S, Giles I, Isenberg D, Lanyon P, Jones A, Marian Regan M, Annie Cooper A, Robert Moots R, Sutcliffe N, Bombardieri M, Pitzalis C, McLaren J, Young-Min S, Dasgupta B, Griffiths B, Dennis D, Mitchell S, Ng W-F. Autonomic symptoms are common and are associated with overall symptom burden and disease activity in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:1973–1979 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
