Peptidylarginine deiminase 1-catalyzed histone citrullination is essential for early embryo development
- PMID: 27929094
- PMCID: PMC5144008
- DOI: 10.1038/srep38727
Peptidylarginine deiminase 1-catalyzed histone citrullination is essential for early embryo development
Abstract
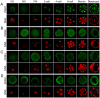
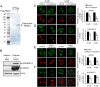
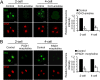
Peptidylarginine deiminase (PADI) enzymes are increasingly being associated with the regulation of chromatin structure and gene activity via histone citrullination. As one of the PADI family members, PADI1 has been mainly reported to be expressed in the epidermis and uterus, where the protein in keratinocytes is thought to promote differentiation by citrullinating filament proteins. However, the roles of PADI1 in preimplantation development have not been addressed. Using a PADI1-specific inhibitor and Padi1-morpholino knockdown, we found that citrullination of histone tails at H4R3 and H3R2/8/17 were markedly reduced in the 2- and 4-cell embryos. Consistent with this observation, early embryo development was also arrested at the 4-cell stage upon depletion of PADI1 or inhibition of PADI1 enzyme activity. Additionally, by employing 5-ethynyl uridine (EU) incorporation analysis, ablation of PADI1 function led to a dramatic decrease in overall transcriptional activity, correlating well with the reduced levels of phosphorylation of RNA Pol II at Ser2 observed at 2- or 4-cell stage of embryos under Padi1 knockdown or inhibiting PADI1. Thus, our data reveal a novel function of PADI1 during early embryo development transitions by catalyzing histone tail citrullination, which facilitates early embryo genome transactivation.
Figures


References
-
- Edwards R. G. Aspects of the molecular regulation of early mammalian development. Reprod Biomed Online 6, 97–113 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Hamatani T., Carter M. G., Sharov A. A. & Ko M. S. Dynamics of global gene expression changes during mouse preimplantation development. Dev Cell 6, 117–131 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Wang Q. T. et al.. A genome-wide study of gene activity reveals developmental signaling pathways in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Dev Cell 6, 133–144 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Jeong H. J. et al.. Gene expression profiling of the pre-implantation mouse embryo by microarray analysis: comparison of the two-cell stage and two-cell block. Theriogenology 66, 785–796 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

