Diaphragm Dysfunction: Diagnostic Approaches and Management Strategies
- PMID: 27929389
- PMCID: PMC5184786
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm5120113
Diaphragm Dysfunction: Diagnostic Approaches and Management Strategies
Abstract
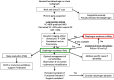
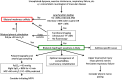
The diaphragm is the main inspiratory muscle, and its dysfunction can lead to significant adverse clinical consequences. The aim of this review is to provide clinicians with an overview of the main causes of uni- and bi-lateral diaphragm dysfunction, explore the clinical and physiological consequences of the disease on lung function, exercise physiology and sleep and review the available diagnostic tools used in the evaluation of diaphragm function. A particular emphasis is placed on the clinical significance of diaphragm weakness in the intensive care unit setting and the use of ultrasound to evaluate diaphragmatic action.
Keywords: diaphragm; diaphragm dysfunction; diaphragm ultrasound; phrenic nerve stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mizuno M. Human respiratory muscles: Fibre morphology and capillary supply. Eur. Respir. J. 1991;4:587–601. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman D.A., Faulkner J.A., Craig A.B., Jr., Maxwell L.C. Performance and histochemical composition of guinea pig and human diaphragm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1973;34:233–237. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez J., Medrano G., Debesse B., Riquet M., Derenne J.P. Muscle fibre types in costal and crural diaphragm in normal men and in patients with moderate chronic respiratory disease. Bull. Eur. Physiopathol. Respir. 1985;21:351–356. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

