Aortic Stiffness as a Surrogate Endpoint to Micro- and Macrovascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 27929441
- PMCID: PMC5187844
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17122044
Aortic Stiffness as a Surrogate Endpoint to Micro- and Macrovascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
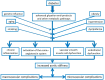
Increased aortic stiffness has been recognized as a predictor of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in some clinical conditions, such as in patients with arterial hypertension and end-stage renal disease, in population-based samples and, more recently, in type 2 diabetic patients. Patients with type 2 diabetes have higher aortic stiffness than non-diabetic individuals, and increased aortic stiffness has been correlated to the presence of micro- and macrovascular chronic diabetic complications. We aimed to review the current knowledge on the relationships between aortic stiffness and diabetic complications, their possible underlying physiopathological mechanisms, and their potential applications to clinical type 2 diabetes management.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity; microvascular and macrovascular complications; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Laurent S., Cockcroft J., van Bortel L., Boutouyrie P., Giannattasio C., Hayoz D., Pannier B., Vlachopoulos C., Wilkinson I., Struijker-Boudier H. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: Methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur. Heart J. 2006;27:2588–2605. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl254. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boutouyrie P., Fliser D., Goldsmith D., Covic A., Wiecek A., Ortiz A., Martinez-Castelao A., Lindholm B., Massy Z.A., Suleymanlar G., et al. Assessment of arterial stiffness for clinical and epidemiological studies: Methodological considerations for validation and entry into the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine registry. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014;29:232–239. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft309. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical