Effects of delayed cord clamping on residual placental blood volume, hemoglobin and bilirubin levels in term infants: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27929530
- PMCID: PMC5334141
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2016.222
Effects of delayed cord clamping on residual placental blood volume, hemoglobin and bilirubin levels in term infants: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: The objective of the study was to measure the effects of a 5-min delay (DCC) versus immediate cord clamping (ICC) on residual placental blood volume (RPBV) at birth, and hemoglobin and serum bilirubin at 24 to 48 h of age.
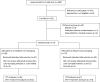
Study design: In this prospective randomized controlled trial, 73 women with term (37 to 41 weeks) singleton fetuses were randomized to DCC (⩾5 min; n=37) or ICC (<20 s; n=36).
Results: Maternal and infant demographics were not different between the groups. Mean cord clamping time was 303±121 (DCC) versus 23±59 (ICC) s (P<0.001) with 10 protocol violations. Cord milking was the proxy for DCC (n=11) when the provider could not wait. Infants randomized to DCC compared with ICC had significantly less RPBV (20.0 versus 30.8 ml kg-1, P<0.001), higher hemoglobin levels (19.4 versus 17.8 g dl-1, P=0.002) at 24 to 48 h, with no difference in bilirubin levels.
Conclusion: Term infants had early hematological advantage of DCC without increases in hyperbilirubinemia or symptomatic polycythemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Comment in
-
Mathematical bias in assessment of placental residual blood volume.J Perinatol. 2017 Oct;37(10):1166. doi: 10.1038/jp.2017.85. J Perinatol. 2017. PMID: 28984874 No abstract available.
-
Response to Rigo et al.J Perinatol. 2017 Oct;37(10):1166. doi: 10.1038/jp.2017.87. J Perinatol. 2017. PMID: 28984875 No abstract available.
References
-
- ACOG. Committee Opinion No. 543: Timing of umbilical cord clamping after birth. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120(6):1522–1526. - PubMed
-
- Yao AC, Lind J. Effect of gravity on placental transfusion. Lancet. 1969;2(7619):505–508. - PubMed
-
- Farrar D, Airey R, Law GR, Tuffnell D, Cattle B, Duley L. Measuring placental transfusion for term births: weighing babies with cord intact. BJOG. 2011;118(1):70–75. - PubMed
-
- Yao AC, Moinian M, Lind J. Distribution of blood between infant and placenta after birth. Lancet. 1969;2(7626):871–873. - PubMed
-
- Oh W, Lind J. Venous and capillary hematocrit in newborn infants and placental transfusion. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1966;55(1):38–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical